Growth Plate Fracture
A broken bone (fracture) in a child or adolescent must be scrutinized. Unlike adults, whose growth plates are closed, a child or adolescent is at risk for a fracture through the growth plate.
A growth plate, also called a physis or physeal plate, is a section of cartilage located at the ends of the long bones in children and teenagers. It is here that cartilage divides and calcifies which adds length and breadth to all the bones in growing individuals. When a person stops growing, usually in mid to late adolescence, the growth plates close or fuse to form solid bone.
Fractures often occur through the growth plate. The physis consists of calcified and uncalcified cartilage. Fractures frequently occur at the junction of these two types of cartilage where the structural matrix of uncalcified cartilage is weaker and less resistant to stresses and strains than the calcified cartilage.*
Growth plate fractures occur when a bone breaks. The growth plate is where new bone develops, so injury to this area can cause the plate to close prematurely and stop bone growth. This may cause a skeletal deformity if not treated properly initially and not monitored long after the fractured bone has healed.
Fractures of the growth plates in the proximal tibia (top of the shin bone) and distal femur (bottom of the thighbone) are the most likely to cause growth arrest or deformity. A child who breaks a growth plate in the leg may develop a limb length discrepancy, where the healthy leg grows longer than the broken leg. (This type of growth deformity should not be confused with bowleg or knock knee, conditions caused by other factors.)
Growth plate injuries are also common in upper extremity long bones, such as the wrist and elbow, and, less commonly, in the shoulder.
Diagnosis
Although a fracture is usually visible on an X-ray, a fracture that includes or is only located in the growth plate may be tricky to diagnose. This is because the growth plate is radiolucent on an X-ray, meaning it is translucent or mostly invisible. Unless the growth plate fracture is displaced (out of alignment) or is part of a fracture that extends from bone that is radiodense (visible as a solid white mass on an X-ray), it can be easy to miss.
Advanced imaging aids in assessing the amount of injury to the growth plate. It is often recommended that children or teenagers who break an arm or leg have a CT scan and/or MRI to determine precisely where the growth plate has been injured. This not only helps in guiding the appropriate treatment of these fractures, but in monitoring growth after the fracture heals.
Growth plate fractures may have no long-term consequences, but they can sometimes cause limb length discrepancies, angular deformities, and/or joint incongruities (in which the two bones that form a joint do not line up properly). Whether such complications arise may depend on the level of energy associated with the injury that caused the break and/or the alignment of the fractured bone during the healing phase.
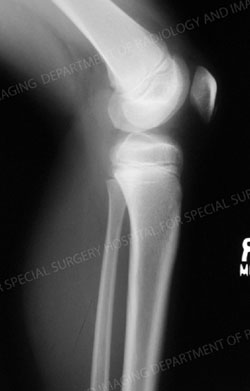
X-ray of a child's knee with a proximal tibia growth plate fracture. The image appears to be that of a healthy knee with no abnormalities because the fracture was exclusively located in the growth plate, and therefore is radiolucent on a plain X-ray. Additional imaging would be required to make a diagnosis.
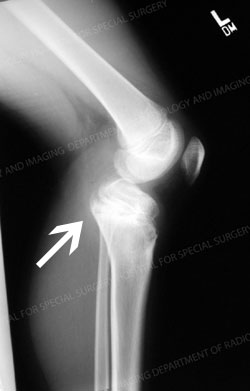
X-ray of the same child nine months after the initial fracture. This image depicts the long-term sequela of a fracture through part of the proximal tibia growth plate. It demonstrates premature closure (arrest) of the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia (front part of the upper shin bone) and illustrates how joint incongruity can ensue.
Treatment
Most growth plate fractures heal with a cast or splint without complication in three to six weeks. Displaced fractures involving the growth plate usually require a doctor to set (manually realign) the bone, which is then casted or splinted. Most children respond well to these procedures. In a small percentage of children, the bone or a portion of the bone will stop growing. This is called "partial growth arrest" or "physeal bar." See image immediately above.
Since there is no way to regenerate the growth plate cartilage after a bony bar forms, additional treatments are required. The size of the bar relative to the entire growth plate determines the methods used to manage the complication. Smaller bars, which are less than half the size of the growth plate, may be resected (removed). The space is then filled with fat or cement. If the bar is greater than half of the growth plate, the remaining viable growth plate is ablated (surgically removed) by a simple procedure to prevent a limb deformity. If patients have a lot of growth remaining, limb lengthening surgery may be performed to lengthen the fractured limb. This way both legs are equal once patients reach their adult height.
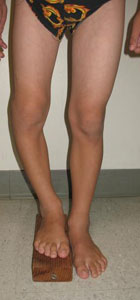
Photo of a child with a limb length discrepancy due to growth plate injury.
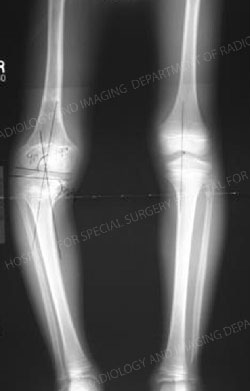
X-ray image of a limb length discrepancy due to growth plate injury.
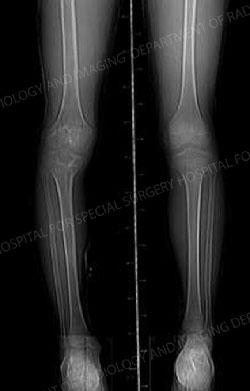
X-ray image of the same child after limb lengthening surgery.
Articles related to growth plate fractures
- Infographic: Growth Plate Injuries in Children and Teens
- Pediatric Sports Injuries: An Overview
- Broken Elbows in Children: An Overview of Elbow Fractures
- Femur Fractures in Children: Treating a Child’s Broken Thighbone
- Pediatric Limb Lengthening: Corrective Surgery for Leg Length Discrepancy in Children
Growth Plate Fracture Success Stories
References
- Goldman V, Green DW. Advances in growth plate modulation for lower extremity malalignment (knock knees and bow legs). Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010 Feb;22(1):47-53. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e328334a600. PMID: 19926991.
- Ruzbarsky JJ, Goodbody C, Dodwell E. Closing the growth plate: a review of indications and surgical options. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2017 Feb;29(1):80-86. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000438. PMID: 27845969.
- * Wenger, DR, Pring, ME: Rang’s Children’s Fractures, Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins, 3rd Ed. 2005.
Updated: 10/13/2023
Reviewed and updated by John S. Blanco, MD; Emily R. Dodwell, MD, MPH, FRCSC; Shevaun Mackie Doyle, MD; Peter D. Fabricant, MD, MPH; Daniel W. Green, MD, MS, FAAP, FACS; Jessica H. Heyer, MD; Ernest L. Sink, MD; David M. Scher, MD; and Roger F. Widmann, MD