Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to produce images. Sound waves are sent and received through a small hand held device known as a transducer. The returning sound waves are used to produce the images. New ultrasound technology allows us to look in great detail at soft tissue abnormalities around joints, tendons, and muscles. In experienced hands, it is a highly accurate technique, which can be used to diagnose a large variety of soft tissue abnormalities.
Hospital for Special Surgery has expertise in musculoskeletal ultrasound which is not readily available at routine ultrasound departments. Below are a number of frequently asked questions about musculoskeletal ultrasound:
Why has my doctor ordered an ultrasound?
Ultrasound provides information for your doctor about the specific soft tissue structure being examined, or about the blood flow in vessels within the soft tissues. Soft tissue structures include a mass in or around a joint, or in a muscle or within your abdomen or pelvis. You may be familiar with the role of ultrasound used during pregnancy, to examine your gall bladder or your kidneys.
Schedule an ultrasound exam at HSS. (A prescription is required.)
You may also be familiar with the term Doppler imaging, which provides blood flow information in both arteries and veins. Abnormal blood flow can be seen in a variety of inflammatory conditions, and at HSS, Doppler is used to examine soft tissues for inflammation.
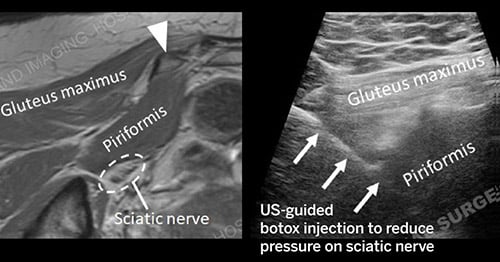
In addition to the diagnostic accuracy, ultrasound guidance for treatment is common at HSS. Because ultrasound images are in "real-time," your doctor may ask us to use ultrasound to help perform procedures, such as withdrawing fluid from a joint or for the injection of medication into a joint or mass. Ultrasound allows the radiologist to continuously monitor real-time the position of a needle in a joint, bursa, cyst, soft tissue mass, etc..., and monitor the progress of an aspiration or injection.
Scheduling forms for ultrasound guided injections of the foot are available to your referring physician to indicate where your symptoms are.
Who performs and interprets ultrasound?
The ultrasound examination will be performed either by a sonologist, who has received training by an accredited institution to perform ultrasound examinations, or by an ultrasound experienced radiologist. Because ultrasound is operator dependent, it will often be the case that the examination will first be performed by the sonologist and the radiologist may come in to post-scan, to further define an area of interest and ensure that the best possible examination is obtained.
What is special about musculoskeletal ultrasound at HSS?
- At HSS, the radiologist performing and/or interpreting your examination has expertise in all aspects of soft tissue and bone imaging, in addition to ultrasound training.
- Highly detailed musculoskeletal ultrasound studies are performed as the routine, not the exception.
- Ultrasound is used to guide injections for delivery of medication (corticosteroids, anaesthetic, etc. into joint, tendon, bursa, cyst, ganglions and neuromas.
- We offer ultrasound-guided calcium aspirations, platelet-rich plasma injections and cryoablation.
- Protocol for evaluation of DVT (deep venous thrombosis) studies includes evaluation of the entire leg-thigh to ankle as the routine, not the exception.
- Highly specialized pediatric evaluations are performed.
- Ultrasound gel is kept specially warm to increase patient comfort and satisfaction.
- Highly skilled sonologists perform the initial prescribed diagnostic scans.
- Accommodation of patients onto the appointment schedule on an as needed basis.
- The Division of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound is a luminary site for testing ultrasound contrast and transducers for optimal musculoskeletal ultrasound imaging.
How is the ultrasound performed?
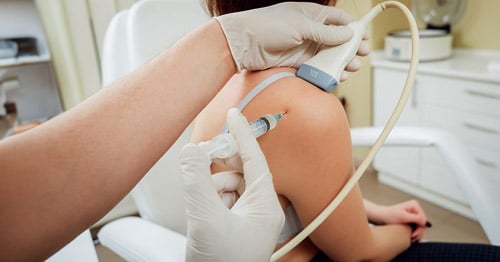
The individual being examined is either seated comfortably in a chair, or lies on a stretcher. Depending on the area to be examined, it may be necessary for you to wear a gown or to assume a particular position, to allow access to the area of concern. A clear gel is applied to the area being examined. The ultrasound transducer is placed directly on the gel to produce images.
What should I do to prepare for the ultrasound?
In most instances, no particular preparation is required. Depending on the area being examined, some initial preparation may be necessary. When looking at the gall bladder, several hours of fasting prior to the exam is required, or when looking at the pelvic organs, it will be necessary to drink water to fill up the bladder. The necessary information will be provided to you at the time the specific exam is scheduled.
What are the risks of ultrasound?
Ultrasound uses non-ionizing radiation and is extremely safe. You may be familiar with the role of ultrasound when it has been used to study the fetus in all phases of development.
What are the alternatives to ultrasound?
Other imaging modalities such as MR or arthrography, may provide similar types of information or complimentary information. An MR examination does not permit aspiration or injection into the involved area. An arthrogram requires use of ionizing radiation and is more invasive. When ultrasound is appropriate, it has the advantage of being readily available, comfortable for most people and less expensive than other types of imaging that may provide comparable information.
What can I expect after the ultrasound examination?
Following an ultrasound examination performed only for diagnostic purposes, you will be able to immediately resume your pre-examination activities. If a therapeutic procedure (injection or aspiration) is performed utilizing ultrasound guidance, in most cases you will be able to resume regular activities within a day. You will receive a post-therapeutic injection information sheet and a one week pain log. You may be monitored for a brief period of time by a nurse following the examination. Significant bleeding or infection are extremely rare complications. If this occurs after you have left the hospital, you should contact your physician as soon as possible or proceed to an emergency facility.
What happens with the results?
The results of the ultrasound examination are determined by both the real time (observed during the examination) and the final static images produced. After the examination, this information will be reviewed by the radiologist in order to generate a written report for your referring doctor. If fluid was aspirated during the examination, the sample will be sent to the laboratory for analysis and the results will be sent to your referring physician. Copies of the report can be obtained through your referring physician's office. Your physician can call the file room at 212.606.1015 and a copy of the report can be faxed or mailed, free of charge, to their office. The radiographs are the property of the institution, as are biopsy slides or blood samples. Copies of the radiographs can be obtained by contacting the file room. There is a charge for obtaining film copies and mailing them to your physician.
Will other tests be ordered?
For some ultrasound procedures, it may be necessary to have a blood test prior to the ultrasound exam. Alternatively, based on the results, the need to perform another imaging study may become apparent. In most cases, however, the ultrasound will be the only test required.
