
Scoliosis / Spine Disorders
Scoliosis and other spine disorders in children such as Scoliosis, kyphosis, spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis, torticollis can be idiopathic (of unknown origin), congenital (present at birth) or neuromuscular (related to nerves and muscles).
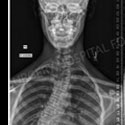
A condition of the spine in which the spine curves to varying degrees in an "S" shape, either to the right or left.
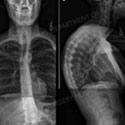
Kyphosis is a forward curvature of the spine in which the spine curves forward creating a round back appearance, or “C” shape.

A common cause of lower back pain in adolescent athletes is a stress fracture in one of the bones (vertebrae) that make up the spinal column, a condition known as spondylolysis. In some cases, the stress fracture can weaken the bone, causing the vertebra to shift out of place, a condition known as spondylolisthesis.

Congenital muscular torticollis (CMT) is a musculoskeletal condition observed at birth or in infancy characterized by shortening of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle on the side of the neck.
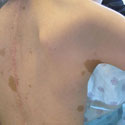
Neurofibromatosis (NF1 and NF2) is a genetic disorder characterized by tumors or neurofibromas that grow in the nervous system and under the skin. Children with NF1 frequently develop orthopaedic problems like scoliosis and tibial dysplasia.

