Glenoid Labrum Tear
A labrum is a cup-shaped rim of cartilage that lines and reinforces a ball-and-socket joint, such as the hip or shoulder.
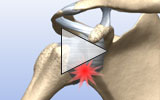
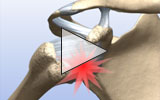
In the shoulder joint, the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) functions as the ball and the glenoid cavity of the scapula functions as the socket. The shoulder labrum, also known as the glenoid labrum, is the attachment site for ligaments and provides support for shoulder joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. It contributes to shoulder stability.
Types of shoulder labral tears
The two most common types of labral injuries in the shoulder are SLAP tears and Bankart tears (also known as Bankart lesions).
SLAP tear
SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior." This type of labral tear occurs where the labrum connects to the biceps tendon.
Bankart tear
In a Bankart tear, a dislocation of the shoulder joint leads the head of the humerus to tear the labrum as it pops out of the socket, usually toward the front, but sometimes toward the back of the shoulder.
Causes of a torn shoulder labrum
SLAP tears can be caused by falling onto an outstretched hand, quickly lifting a heavy object or from a forceful, overhead arm motion. A dislocated shoulder that causes a Bankart tear can occur during sports activity or trauma, such as a fall.
SLAP tears are frequently experienced by athletes of sports that involve overhead throwing, such as tennis, baseball, football and javelin or shotput. Bankart tears are usually experienced by younger patients, typically in their twenties. Labral tears caused by trauma, such as falling down a flight of stairs, are especially common among older adults, since cartilage becomes more brittle with age.
Symptoms of a torn glenoid labrum
Common symptoms in both types include dull or aching pain in the shoulder and difficulty performing normal shoulder movements. Instability caused by a Bankart lesion may lead to frequent shoulder dislocations. A SLAP tear often causes pain at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon.
Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment
With rest and physical therapy, some minor labral tears may heel sufficiently in people who do not plan to engage in competitive athletics or heavy overhead arm motion. In a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, it may be possible to pop the shoulder back into place and follow up with physical therapy.
But athletes and other active individuals, such as those whose professions require overhead lifting, will usually need surgery.
Surgical treatment
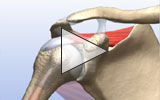
Surgery for a torn shoulder labrum can often be performed arthroscopically, using minimally invasive techniques. Depending on the type of tear and the severity, the labrum and ligaments may need to be reattached to the bone using sutures and anchors.
Shoulder labral tear surgery animations
These videos provide animated views of various surgical treatments for a torn shoulder labrum.
Detailed content on shoulder labral tears
For a deeper dive on this topic, read the article below.
Articles on topics related to tears of the shoulder labrum
Learn more about arthroscopic surgery of the shoulder and labrum injury prevention.
Glenoid Labrum Tear Success Stories
In the news