Arthritis of the Back and Neck
Arthritis of the spine refers to inflammation in joints that make up the spine. Spinal arthritis conditions fall into two general categories, based upon their discrete causes: degenerative arthritis (also known as osteoarthritis) and inflammatory arthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the spine
Osteoarthritis is a caused by degenerative changes in a person's spinal joints that occurs due to years of use as a person ages. Osteoarthritis of the back or neck, also known as spondylosis, is much more common than is inflammatory arthritis. Nearly all elderly people will have some degree of spondylosis, whether or not it causes any symptoms. It can also occur in younger people, however.
Symptoms range from none to feelings stiffness and/or pain in the neck or back, and/or pain that radiates to shoulders, arms or legs. Osteoarthritis of the spine causes the joints along the spine to deteriorate, which may result in the formation of bone spurs, cysts and/or a narrowing of the disc space. It is also a common cause of spinal stenosis, radiculopathy and myelopathy.
Low back pain caused by osteoarthritis
The most common symptom of spinal osteoarthritis is pain in the lumbar spine (low back – see further below for an explanation of spine anatomy). This pain may also radiate down to the pelvis, buttocks, groin or thighs. It is usually treated through a combination of:
- physical therapy and exercise that strengthens a person's core (such as yoga, Pilates or aquatic therapy)
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and/or adjuvant pain medication
When these treatments are not enough to alleviate pain and stiffness, a patient may require procedural pain management, such as corticosteroid injections or blocking of the medial nerve through radiofrequency ablation, where heat generated by radio waves disrupts the nerve’s ability to transmit pain signals.
Neck pain caused by osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the neck, called cervical spondylosis, is also common. This is characterized by arthritic deterioration of the discs and facet joint cartilage of the cervical spine. Some people experience no symptoms, while others may feel stiffness and/or pain in the neck, shoulders and/or between the shoulder blades. (See also Cervical Radiculopathy.)
Animation on osteoarthritis of the spine.
Inflammatory arthritis of the spine
Inflammatory arthritis refers to various chronic, autoimmune disorders that cause joint inflammation. Forms of inflammatory arthritis of the spine, known as spondyloarthritis, include ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis (formerly known as Reiter's syndrome), psoriatic arthritis and other conditions.
These conditions can affect adults and children alike. Symptoms vary, but some forms are characterized by low back and/or neck pain, morning stiffness, and limited motion in the back which are typically improved through exercise and return after periods of rest. Patients with some inflammatory conditions of the spine, such as ankylosing spondylitis, may have their back symptoms overshadowed by pain and inflammation of other joints, such as the knees, hips, shoulders, wrists, etc.
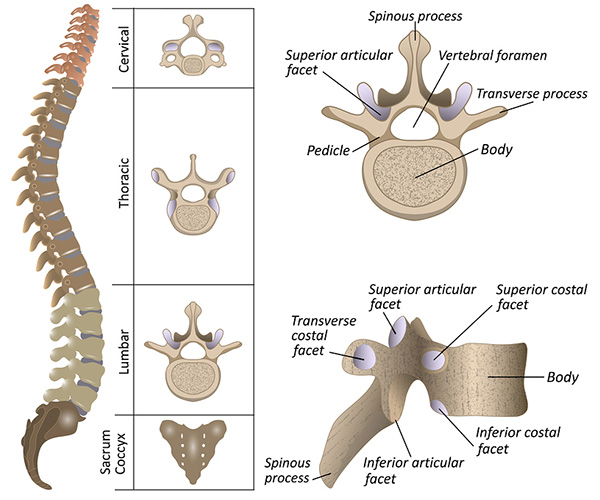
Anatomy of the spine
The bones that compose the spine (or backbone) are divided into four basic segments. From top to bottom, these are:
- The cervical spine (the neck) – the first seven vertebrae located just below the skull
- The thoracic spine – the 12 vertebrae of the upper back
- The lumbar spine – the five vertebrae of the lower back
- The sacral spine – composed of a triangular structure called the sacrum (five individual vertebrae that fuse together between the age of 18 and 30) and the coccyx (commonly called the tailbone and composed of three to five individual vertebrae, some of which may fuse together in adulthood)
Articles on arthritis of the spine
Get more information on degenerative and autoimmune arthritis conditions that affect the spine.
Articles related to spinal arthritis and noninvasive treatments
Learn about various disorders that may be caused by or associated with arthritis of the spine, as well as potential nonsurgical treatments.
- Facet Joint Injection
- Degenerative Scoliosis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
- An Overview of Lower Back Pain
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis − An Overview
- Cervical Radiculopathy: Pinched Nerve in the Neck and Nonsurgical Treatments
- Cervical Myelopathy: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Frequently Asked Questions
Articles on orthopedic surgeries related to spinal arthritis
Spinal arthritis usually does not require surgery unless there is additional condition causing pain, which may benefit from a spinal decompression or fusion surgery.
- LLIF/XLIF Surgery: Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- ACDF Surgery: Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
- Spine Surgery: Posterior Cervical Laminotomy
- Instrumented Cervical Laminectomy, Fusion
- Lumbar Fusion
- ALIF Surgery: Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- PLIF Surgery: Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- TLIF Surgery: Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Minimally Invasive Lower Back Surgery for Disc Degeneration: The Anterolateral (Side) Approach
- Spine Surgery: Lumbar Vertebral Body Replacement
Arthritis of the Back and Neck Success Stories
Updated: 9/9/2022
References
- Caridi JM, Pumberger M, Hughes AP. Cervical radiculopathy: a review. HSS J. 2011 Oct;7(3):265-72. doi: 10.1007/s11420-011-9218-z. Epub 2011 Sep 9. PMID: 23024624; PMCID: PMC3192889.
- Kiely PD, Quinn JC, Du JY, Lebl DR. Posterior surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: review article. HSS J. 2015 Feb;11(1):36-42. doi: 10.1007/s11420-014-9425-5. Epub 2015 Feb 10. PMID: 25737667; PMCID: PMC4342399.


