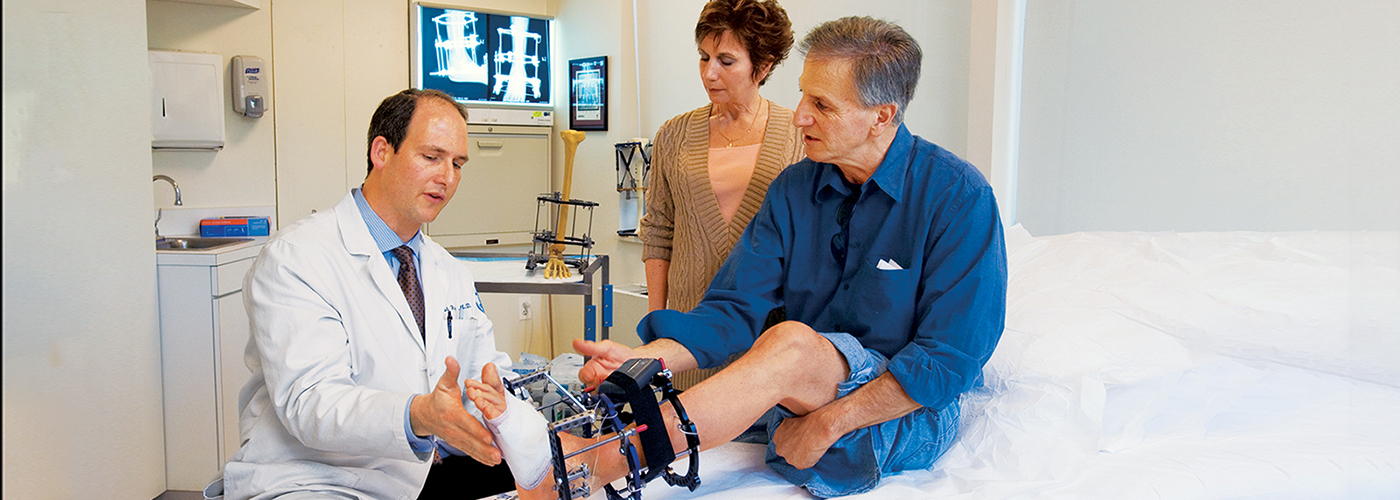
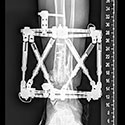
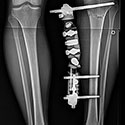
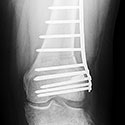
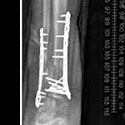
Limb Lengthening and Complex Reconstruction Service
The HSS Limb Lengthening and Complex Reconstruction Service specializes in limb lengthening and deformity correction for adults and children. Our unique skill with a variety of bone reconstruction techniques enables us to sculpt bone and even create bone where there was none.We provide opportunities for individuals who previously had no treatment alternatives.
Comprehensive Care
A consultation at our Center involves a thorough examination, analysis and discussion before we provide a sophisticated diagnosis and course of treatment. Our synergetic relationship within HSS and other departments provides access to state-of-the-art orthopedic equipment and other bone health experts. From your first appointment to your recovery and rehabilitation, you can expect us to provide in-depth education, personalized recommendations and high-quality care.
Please see our areas of expertise, before and after photos and more information below:
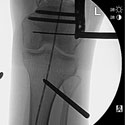
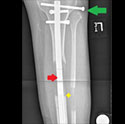
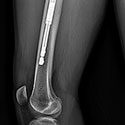
Internal Bone Lengthening: Motorized PRECICE STRYDE Nail
This state-of-the-art treatment for leg length discrepancy gradually lengthens the femur, tibia, and humerus with a remote control device and is used when external fixation is not needed.
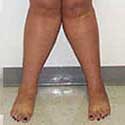
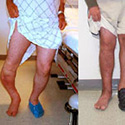
Knock Knee, Bowleg and Limb Malalignment
Pain in the hip, knee, and ankle can often be caused by bowlegs (varus deformity) or knock knees (valgus deformity). This often leads to pain, cosmetic deformity, and premature knee arthritis.
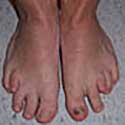
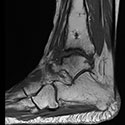
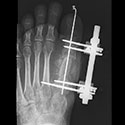
Foot and Ankle Deformity
Complex foot and ankle deformity may require gradual correction, treatment for infection and bone loss in the ankle, joint preservation with ankle distraction surgery, and metatarsal foot lengthening.
Bone Trauma: Nonunion and Malunion
Problems with bone healing, alignment, or infection can occur after trauma. Nonunion is when the bone does not heal properly and malunion is when the bone becomes deformed or shortens the limb.
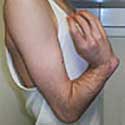
Upper Extremity Lengthening and Deformity Correction
Advanced techniques can restore symmetry and function after infection, trauma, or benign tumors damage the shoulder growth plates and cause shortening and deformity of the humerus (upper arm).
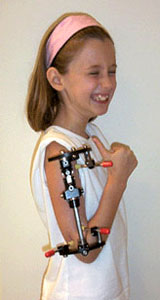
Limb Lengthening for Kids and Teens
The growth potential in children sets them apart. We can reliably equalize limb length, correct deformities, and even increase stature in select conditions, while protecting the growth plates.
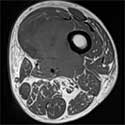
Bone Tumors and Lesions
We diagnose and treat benign and malignant bone tumors, including the reconstruction of missing bone (bone transport), limb lengthening and deformity correction.
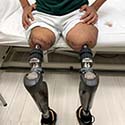
Limb Salvage and Amputation Reconstruction Center
Our Center provides bone transport to replace missing bone and osseointegration limb replacement for patients who have undergone amputation and have difficulty with socket prostheses.
Osseointegration Limb Replacement Center
The first to use osseointegration for transtibial amputations in the United States, we offer personalized solutions and the most cutting-edge techniques for those who have had or need lower or upper limb amputation.
About Limb Lengthening
A History of Limb Lengthening: Proven, Powerful and Effective
Limb lengthening is possible and has been performed successfully for over 50 years in Kurgan, Russia. Gavriil A. Ilizarov developed the concept in 1951 after seeing many WWII veterans who had leg fractures that had not healed (nonunions).
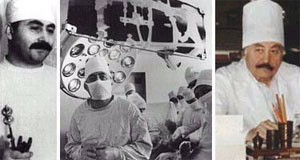 Ilizarov first developed an external fixation frame that was placed around the leg. Knowing that compression of the fracture would help stimulate bone healing, he built a frame that had this capacity. He instructed a patient to gradually compress the nonunion by turning a rod. However, the patient turned the rod the wrong way and caused distraction (separation) of the fracture. Ilizarov noticed that new bone had formed in the gap between the bone ends. This was the beginning of much research and development that showed that limb lengthening was possible, safe and effective.
Ilizarov first developed an external fixation frame that was placed around the leg. Knowing that compression of the fracture would help stimulate bone healing, he built a frame that had this capacity. He instructed a patient to gradually compress the nonunion by turning a rod. However, the patient turned the rod the wrong way and caused distraction (separation) of the fracture. Ilizarov noticed that new bone had formed in the gap between the bone ends. This was the beginning of much research and development that showed that limb lengthening was possible, safe and effective.
Ilizarov and his colleagues performed thousands of limb lengthening procedures in Kurgan, Russia. Russian politics, however, made education and communication with the Western world very difficult. Finally, Italian surgeons started performing and improving the procedure in the early 1980s and a large center soon developed in Lecco, Italy. The first limb lengthening case in the United States was performed in 1988. At first, there was much resistance and skepticism from the US orthopedic community, but limb lengthening has proven to be a very powerful and effective procedure.
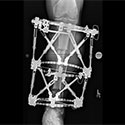
Limb lengthening and reconstruction techniques can be used to replace missing bone and lengthen and/or straighten deformed bone segments. The procedures may be performed on both children and adults who have limb length discrepancies due to birth defects, diseases or injuries. The limb lengthening and deformity correction process works on the principle of distraction osteogenesis. This is a revolutionary concept that reverses the long-held belief that bone cannot be regenerated. In this process, a bone that has been cut during surgery can be gradually distracted (pulled apart), leading to new bone formation (osteogenesis) at the site of the lengthening. In this way, bone segments can be lengthened by 15 to 100 percent of their original length. We use a variety of techniques, including the use of monolateral (one-sided) and circular external fixation devices, to correct angular deformities as well as limb length discrepancies.
 The regenerated bone is normal and does not wear out. The muscles, nerves and blood vessels grow in response to the slow stretch like they do during a growth spurt or in pregnancy. The actual procedure is minimally invasive and requires only one or two nights in the hospital. Patients aren't in much pain since the distraction is so gradual and patients can continue to walk during the treatment.
The regenerated bone is normal and does not wear out. The muscles, nerves and blood vessels grow in response to the slow stretch like they do during a growth spurt or in pregnancy. The actual procedure is minimally invasive and requires only one or two nights in the hospital. Patients aren't in much pain since the distraction is so gradual and patients can continue to walk during the treatment.
Children and adults can be appropriate candidates for the procedure. Children with congenital deformities such as fibular hemimelia, congenital short femur and hemiatrophy will often have unequal leg length and this may be associated with deformity. Many adults have had this condition since childhood and have developed back pain and hip arthritis from the leg length discrepancy. Growth plate fractures and bone infections in children can cause stunting of growth that results in discrepancy.
Following trauma, bones can heal in a shortened and deformed position (malunion). Sometimes the bone can even remain unhealed (nonunion). Limb lengthening procedures address all of these issues. We have been able to successfully correct large deformities and equalize limbs with discrepancies of several inches. A segment of bone can be missing after a bone tumor, bone infection or severe fracture. We can transport new bone to fill in this defect.
Short stature can be very disabling in patients with dwarfism, for example. We can lengthen both legs simultaneously to increase stature. We have been able to lengthen achondroplastic dwarf patients 12 inches in the legs and five inches in the arms. This allows them to function more independently and be able to reach the telephone, toilet and gas pedal, for example.
Young adult patients with leg deformities are at risk for developing arthritis as a result of their malalignment. These same techniques can be used to correct severe deformities safely and avert the need for joint replacement.
For more information read Dr. Rozbruch's article on Limb Lengthening - An Overview.
Surgeons
Staff
Who is a good candidate for limb lengthening?
Patients come to HSS to receive the best care available, and it is our mission to ensure each patient we meet gets the best. To that end, we are dedicated to providing services that are within our expertise and referring patients to others master physicians for procedures we do not perform. This ensures the highest standard of patient care.
There are many different kinds of patient conditions that benefit from limb lengthening and complex reconstruction surgery. This includes both upper and lower extremity and both children and adults. The etiology may be after trauma or from birth. The challenge may be limb length discrepancy and/or limb mal-alignment.
Adults and Children
- Arm or leg length differences
- Bone or joint deformity
Congenital Deformities
(birth defects)
- Congenital short femur
- Fibular hemimelia
- Hemiatrophy
Short Stature
- Dwarfism
- Constitutional short stature
After Trauma
- Growth plates fractures
- Malunion
- Nonunion
- Shortening & deformity
- Bone defects
After Infection
- Osteomyelitis- bone infection
After Tumor
- Bone defects
Preparing Our Patients for Surgery with Preoperative Patient Education
Preoperative education about your procedure will aid in your recovery. We want you to understand the details of your procedure and the usual in hospital and post-operative routine. A better understanding of your procedure will empower you to participate in your care and know what to expect during the recovery.
- Limb Deformity Correction with Internal Fixation
- Limb Deformity Correction and Lengthening with External Fixation
- Limb Lengthening with the PRECICE Internal Lengthening Rod
- Ankle Distraction
- Ankle Fusion
Other Educational Materials
- Ankle Arthritis: When to Distract, Fuse or Replace (YouTube video - Dr. Rozbruch)
- Precice internal lengthening nail remote control device (YouTube video - Dr. Rozbruch)
- Mini Rail Adjustment (YouTube video - Dr. Fragomen)
- Strut Adjustment (YouTube video - Dr. Fragomen)
- Strut Change (YouTube video - Dr. Fragomen)
- Adult Rail Adjustment (YouTube video - Dr. Fragomen)
- Frame Adjustments - Monolateral Frame (YouTube video - Dan Bigman, PA)
- Pin Care Brochure (pdf)
- Pin Care - Monolateral Frame (YouTube video - Dan Bigman, PA)
- Recommendations for Minimizing Scars (pdf - Dan Bigman, PA)
- Automobile Hand Control Dealers (pdf)
- Parent Organizer (pdf - tips for parents from parents)
Includes: Logs for doctor's appointments, insurance, home care, physical therapy, gifts, and useful tips when a family member is undergoing a major medical procedure. - Staged Bilateral Surgery Timeline (pdf)
- Recovery Guide after Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery (pdf)
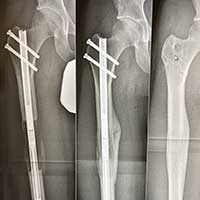
Before and After Photos
Patient Videos
For additional patient videos, click the menu button ![]() in the upper right corner of the video player.
in the upper right corner of the video player.
Read more patient stories.
Patient Case Histories
Post-operative Physical Therapy Videos
Physical Therapy Guides
Postoperative Physical Therapy Guide
Covers exercises for the tibia, femur, hinged foot/ankle, and the fixed foot/ankle.
Phase II Strengthening Exercises
Covers exercises for limb lengthening phase II.
Tibial and Femoral Osteotomy
Contains rehabilitation exercises and challenges presented after surgery.
Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Internal Lengthening Nail
Contains postsurgical rehabilitation exercises.
Fellowship
During the Limb Lengthening and Complex Reconstruction Fellowship, fellows become proficient in the diagnosis, management, decision-making, and surgical techniques associated with limb lengthening and reconstruction. The fellow will gain both clinical and research experience. The Ilizarov method is extensively used in addition to more conventional approaches. This will include preoperative, surgical, and postoperative care. There will also be opportunities for basic and clinical research.
Publications
Research is an integral part of the innovation and advancement of our specialty. These publications reflect the breadth of research from the Limb Lengthening and Complex Reconstruction Service at HSS.
2020
- David T. Zhang, Peter S. Principe, Austin T. Fragomen, S Robert Rozbruch. Comparison and Validation of Preoperative Planning Techniques for Distal Femoral Osteotomies and Proximal Tibial Osteotomies. J Knee Surg. May 2020. DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1710372
- Marano AA, Modiri O, Rozbruch SR, Otterburn DM. Soft Tissue Contouring at the Time of Osseointegrated Implant Reconstruction for Lower Extremity Amputation. Ann Plast Surg. 2020 Mar 13. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002329. [Epub ahead of print]
- Dabash S, Buksbaum JR, Fragomen A, Rozbruch SR. Distraction arthroplasty in osteoarthritis of the foot and ankle. World J Orthop 2020; 11(3): 145-157. DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i3.145
- Fragomen A.T., Bernstein M., Rozbruch S.R. Intramedullary Lengthening and Compression Nails. In: Crist B., Borrelli Jr. J., Harvey E. (eds) Essential Biomechanics for Orthopedic Trauma. Springer, Cham. March 2020.
2019
- Lam A, Richardson SS, Buksbaum J, Markowitz J, Henry MW, Miller AO, Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. Chronic Osteomyelitis of the tibia and ankle treated with Limb Salvage Reconstruction. J Bone Jt Infect 2019; 4(6):306-313. doi:10.7150/jbji.40337.
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD, Jason Teplensky, BS, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Intramedullary Nails Perform Poorly in Long-Bone Surgery. HSS Jrnl (2019) 15:109-114. DOI 10.1007/s11420-018-9634-4.
- Austin T. Fragomen, David Wellman, S. Robert Rozbruch The PRECICE magnetic IM compression nail for long bone nonunions: a preliminary report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. June 2019. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-019-03225-4.
- Makhdom, Asim M., MD, MSc, FRCSC; Fragomen, Austin, MD; Rozbruch, S. Robert, MD. Knee Arthrodesis After Failed Total Knee Arthroplasty. JBJS.April 3, 2019 - Volume 101 - Issue 7 - p 650-660. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.18.00191.
- Rachael J. Da Cunha, MD, FRCSC; Andrew P. Kraszewski, PhD; Howard J. Hillstrom, PhD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain. HSS Journal. March 2019. DOI: 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6.
- Peter K. Sculco, MD, Cynthia A. Kahlenberg, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Management of Extra-articular Deformity in the Setting of Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2019;00:1-12. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-18-00361.
- Michael E. Steinhaus, MD; Joshua Buksbaum, BS; Avraham Eisenman, BA; Monal Kohli, MS; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Postoperative Blood Loss in Distal Femoral Osteotomy J Knee Surg. February 2019. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1678540.
- Gruskay, Jordan A., MD; Fragomen, Austin T., MD; Rozbruch, S. Robert, MD. Idiopathic Rotational Abnormalities of the Lower Extremities in Children and Adults. JBJS Reviews. January 2019, Volume 7, Issue 1. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.18.00016
- Green SA, Fragomen AT, Herzenberg JE, Iobst C, McCarthy JJ, Nelson SC, et al. A magnetically controlled lengthening nail: A prospective study of 31 individuals (The PRECICE™ intramedullary nail study). J Limb Lengthen Reconstr 2018;4:67-75. DOI: 10.4103/jllr.jllr_20_18
- Shawn S. Richardson, MD, William W. Schairer, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Cost Comparison of Femoral Distraction Osteogenesis With External Lengthening Over a Nail Versus Internal Magnetic Lengthening Nail. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;00:1-7. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00741.
- Fragomen AT, Kurtz AM, Wagner PJ, Nguyen J, Liu SS, Rozbruch SR. Anesthesia for removal of external fixation with hydroxyapatite-coated half pins. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr 2018;4:90-6. DOI: 10.4103/jllr.jllr_29_17
2018
- Fragomen, A.T., McCoy, T.H. & Fragomen, F.R. A Preliminary Comparison Suggests Poor Performance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Versus Titanium Plates in Distal Femoral Osteotomy. HSS Journal October 2018, Volume 14, Issue 3, pp 258–265. DOI: 10.1007/s11420-017-9587-z
- Evan D. Sheha, MD; Michael E. Steinhaus, MD; Han Jo Kim, MD; Matthew E. Cunningham, MD, PhD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Leg-Length Discrepancy, Functional Scoliosis, and Low Back Pain. JBJS Reviews 2018;6(8):e6. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00148.
- James Barger, BA; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Antibiotic-Coated Interlocking Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of Long-Bone Osteomyelitis. JBJS Reviews. 5(7):e5, JUL 2017. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.16.00095.
- Ettore Vulcano, MD; Jonathan S. Markowitz, BS; Shabaz Ali; Joseph Nguyen, MPH; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;26:e388-e394. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00949.
- Mitchell Bernstein, MD, FRCSC; Austin Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Tibial Bone Transport Over an Intramedullary Nail Using Cable and Pulleys. JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques March 2018, 8(1):e9(1-12). DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.17.00035
- Reggie C. Hamdy, MD, MSc, FRCS(C); Mitchell Bernstein, MD, FRCS(C); Austin T. Fragomen, MD; and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. What’s New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1436-42 DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.18.00584
- Robert L. Buly, MD, MS; Branden R. Sosa, HS; Lazaros A. Poultsides, MD, MSc, PhD; Elaine Caldwell, BS, RN; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Femoral Derotation Osteotomy in Adults for Version Abnormalities. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;00:1-10. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00623.
- Christopher A. Lobst; S. Robert Rozbruch; Scott Nelson; Austin Fragomen. Simultaneous Acute Femoral Deformity Correction and Gradual Limb Lengthening Using a Retrograde Femoral Nail: Technique and Clinical Results. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;26:241-250. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00573.
- Laura J. Kleeblad, MD; Jelle P. van der List, MD; Andrew D. Pearle, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Predicting the Feasibility of Correcting Mechanical Axis in Large Varus Deformities With Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. The Journal of Arthroplasty 33 (2018) 372-378. DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.09.052.
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD, Anton M. Kurtz, MD, Jonathan R. Barclay, BS, Joseph Nguyen, MPH, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. A Comparison of Femoral Lengthening Methods Favors the Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail When Compared with Lengthening Over a Nail. HSS Jrnl (2018). DOI: 10.1007/s11420-017-9596-y
2017
- Fragomen, A.T., McCoy, T.H. & Fragomen, F.R. A Preliminary Comparison Suggests Poor Performance of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Versus Titanium Plates in Distal Femoral Osteotomy. HSS Jrnl (Dec 2017). DOI: 10.1007/s11420-017-9587-z
- Austin T. Fragomen & S. Robert Rozbruch (2017) Retrograde magnetic internal lengthening nail for acute femoral deformity correction and limb lengthening, Expert Review of Medical Devices, 14:10, 811-820, Oct 2017. DOI: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1378092
- Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults with Brachymetacarpia.Aaron Lam, Austin T. Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. Hand (N Y). Oct 2017. DOI: 10.1177/1558944717736859.
- Distal Femoral Flexion Deformity From Growth Disturbance Treated With a Two-Level Osteotomy and Internal Lengthening Nail. Austin T. Fragomen and Fiona R. Fragomen. Strat Traum Limb Recon. Oct 2017. DOI: 10.1007/s11751-017-0298-2
- Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Multifactorial Perceived Limb Length Discrepancy. Amgad M. Haleem, Kevin F. Wiley, Raul Kuchinad, S. Robert Rozbruch. The Journal of Arthroplasty Volume 32, Issue 10, Oct 2017.
- What's New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction. Reggie C. Hamdy; Mitchell Bernstein; Austin T. Fragomen; S. Robert Rozbruch. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 99(16):1408–1414, Aug 2017. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00464.
- Circular hexapod external fixation for periprosthetic tibial fracture. Michael J. Assayag, MD, FRCSC, Noam Bor, MD, Guy Rubin, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Arthroplasty Today (June 2017). DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2017.03.001
- Does the Surgical Correction of Tibial Torsion with Genu Varum Produce Outcomes Similar to Those in Varus Correction Alone? Austin T. Fragomen MD, Matthew Meade OMS, Eugene Borst BS, Joseph Nguyen MPH, S. Robert Rozbruch MD. J Knee Surg, June 2017. DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1603797.
- Transitioning to an Intramedullary Lengthening and Compression Nail. Fragomen AT. J Orthop Trauma Vol 31, Number 6 Supplement, June 2017.
- Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail. S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. J Orthop Trauma Vol 31, Number 6 Supplement, June 2017. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000843.
- Humerus Lengthening With the PRECICE Internal Lengthening Nail. Anton M. Kurtz, MD and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. J Pediatr Orthop Vol 37, Number 4, June 2017. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000941.
- Patellar instability treated with distal femoral osteotomy. Ishaan Swarup, Osama Elattar and S. Robert Rozbruch. Knee, The, Volume 24, Issue 3, Pages 608-614, June 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2017.02.004
- Humeral Lengthening with the PRECICE Magnetic Lengthening Nail. Hammouda, A.I., Standard, S.C., Rozbruch, S.R., Herzenberg J.E. HSS Jrnl (April 2017) 13: 217. DOI: 10.1007/s11420-017-9552-x
- Lengthening and deformity correction about the knee using a magnetic internal lengthening nail. Austin T. Fragomen and S. Robert Rozbruch. SICOT J 2017, 3, 25. March 2017. DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017014
- Correction of tibial malunion in a patient with ipsilateral total knee and ankle prostheses using external ring fixation and the ilizarov method. Smith AM, Haleem AM, Fragomen AT, Ellis SJ. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr Jan 2017;3:65-9.
- Why are we special? Limb deformity is more than an overlapping subspecialty.Rozbruch SR. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr Jan 2017;3:1-3.
- Tibial/Femoral Osteotomy. Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. In Green A, and Hayda R: Orthopaedic Postoperative Rehabilitation. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; Jan 2017
2016 and earlier
2016
- Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty: Indications, Technique, and Outcomes. Mitchell Bernstein, Jay Reidler, Austin Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2016;0:1-11. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00077
- Prophylactic Postoperative Antibiotics May Not Reduce Pin Site Infections After External Fixation. Austin T. Fragomen, Andy O. Miller, Barry D. Brause, Vladimir Goldman, and S. Robert Rozbruch. The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. Vol. 12 No. 3; October 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11420-016-9539-z
- Neglected Patellar Tendon Rupture with Massive Proximal Patellar Migration Treated with Patellar Transport and Staged Allograft Reconstruction. Osama Elattar, MD, Struan H. Coleman, MD, Russell F. Warren, MD,and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. The Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 4(11), 2325967116672175. DOI: 10.1177/2325967116672175
- Validation of a modified Scoliosis Research Society instrument for patients with limb deformity: The limb deformity‑Scoliosis Research Society (LD-SRS) score. Peter D. Fabricant, Eugene W. Borst, Stuart A. Green, Robert G. Marx, Austin T. Fragomen, and S. Robert Rozbruch. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2.
- Gradual correction of knee flexion contracture using external fixation. Ettore Vulcano, Jonathan S. Markowitz, Austin T. Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2.
- Oxygen consumption testing and self‑reported outcomes following limb salvage with tibiocalcaneal or tibio‑talo‑calcaneal fusion. S. Robert Rozbruch, Joshua R. Buksbaum, Austin T. Fragomen, Eugene W. Borst, Polly DeMille. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2
- Open Wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy: Accuracy of Correction and Patient Outcomes. Osama Elattar, Ishaan Swarup, Aaron Lam, Joseph Nguyen, Austin Fragomen and S. Robert Rozbruch. The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. 5 July 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11420-016-9516-6
- The use of blocking screws with internal lengthening nail and reverse rule of thumb for blocking screws in limb lengthening and deformity correction surgery. Muthusamy S, Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. Strat Traum Limb Recon. 11 September 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0265-3
- What's New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction. Hamdy RC, Bernstein MA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 17 August 2016. DOI 10.2106/JBJS.16.00460
- Lengthening of the Femur with a Remote-Controlled Magnetic Intramedullary Nail: Retrograde Technique. Austin T. Fragomen, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, JB&JS Essential Surgical Techniques, Volume 6, Issue 2, May 11, 2016
- Prevention of pin site infection in external fixation: A review of the literature. Kazmers NH, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction. 3 May 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0256-4
- External fixation reconstruction of the residual problems of benign bone tumours. Levent Eralp, F. Erkal Bilen, S. Robert Rozbruch, Mehmet Kocaoglu, Ahmed I. Hammoudi, Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction, 26 January 2016.
- Lengthening of the Femur with a Remote-Controlled Magnetic Intramedullary Nail: Antegrade Technique. S. Robert Rozbruch, Austin T. Fragomen, JB&JS Essential Surgical Techniques, Volume 6, Issue 1, January 13, 2016.
2015
- Talar body fracture nonunion and osteonecrosis with adjacent arthritis can be successfully treated with tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis using circular external fixation. Eugene Wilson Borst, Scott J. Ellis, Austin Thomas Fragomen. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Oct-Dec 2015, Vol 1, Issue 1.
- Distraction osteogenesis for brachymetatarsia: Clinical results and implications on the metatarsophalangeal joint, Amgad M. Haleem, Angela Balagadde, Eugene Wilson Borst, Huong T. Do, Austin Thomas Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch, Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction, Oct-Dec 2015, Vol 1, Issue 1
- Complex Ankle Arthrodesis: Review of the literature, Remy V Rabinovich, Amgad M Haleem, S Robert Rozbr, World Journal of Orthopedics, 2015 September 18; 6(8): 602-613 ISSN 2218-5836
- Skeletal Repair in Distraction Osteogenesis: Mechanisms and Enhancements, Jocelyn Compton, Austin Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch, JBJS Reviews, Volume 3, Issue 8, August 2015, DOI 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.N.00107
- Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery Case Atlas, Springer International Publishing, Editors: Rozbruch, S. Robert, Hamdy, Reggie (Eds.) Copyright: 2015
3 book set, 2500 pages. The atlas features six sections all pertaining to limb deformity correction: Pediatric Deformity, Trauma, Foot & Ankle (edited by Dr. Fragomen), Adult Deformity (edited by Dr. Rozbruch), Tumor, and Upper Extremity - What is the Utility of a Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Service in an Academic Department of Orthopaedic Surgery?; S. Robert Rozbruch, Elizabeth S. Rozbruch, Samuel Zonshayn, Eugene W. Borst & Austin T. Fragomen; Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research; Volume 473, Number 4; DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4267-0
2014
- Does Integrated Fixation Provide Benefit in the Reconstruction of Post-Traumatic Tibial Bone Defects?; Symposium: 2014 Annual Meeting of the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society; Mitchell Bernstein MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Samir Sabharwal BA, Jonathan Barclay BA, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4326-6
- Metatarsophalangeal Arthritis Following Fourth Metatarsal Lengthening Treated With Distraction Arthroplasty: Case Report, Amgad M. Haleem, Douglas N. Mintz and S. Robert Rozbruch, Foot Ankle Int 2014 35: 1075 originally published online 18 July 2014 DOI: 10.1177/1071100714543648
- Knee Arthrodesis as Limb Salvage for Complex Failures of Total Knee Arthroplasty, Raul Kuchinad, MD, FRCSC, Mitchell S. Fourman, MD M.Phil, Raul Kuchinad, MD, FRCSC, Mitchell S. Fourman, MD M.Phil, The Journal of Arthroplasty 29 (2014) 2150–2155
- Neglected rotatory knee dislocation: A case report, Saker Khamaisy, Amgad M. Haleem, Riley J. Williams, S. Robert Rozbruch, S. Khamaisy et al. / The Knee 21 (2014) 975–978
- What Risk Factors Predict Usage of Gastrocsoleus Recession During Tibial Lengthening? S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Samuel Zonshayn BA, Saravanaraja Muthusamy MBBS, MS, Ortho, Eugene W. Borst BA, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Joseph T. Nguyen MPH, Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3526-9
- Motorized Intramedullary Nail for Management of Limb-length Discrepancy and Deformity. S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; John G. Birch, MD; Mark T. Dahl, MD; John E. Herzenberg, MD, J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2014;22:403-409, July 2014, Vol 22, No 7
- Development and validation of a computational model of the knee joint for the evaluation of surgical treatments for osteoarthritis. R. Mootanah, C.W. Imhauser, F. Reisse, D. Carpanen, R.W. Walker, M.F. Koff, M.W. Lenhoff, S.R. Rozbruch, A.T. Fragomen, Z. Dewan, Y.M. Kirane, K. Cheah, J.K. Dowella and H.J. Hillstrom, Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 2014 Vol. 17, No. 13, 1502–1517
- Precision of the PRECISE ® Internal Bone Lengthening Nail, Yatin M. Kirane, Austin T. Fragomen, and S. Robert Rozbruch, Clin Orthop Relat Res. ISSN 0009-921X, DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3575-0, 2014
- Recombinant Human BMP-2 Increases the Incidence and Rate of Healing in Complex Ankle Arthrodesis, Fourman MS, Borst EW, Bogner E, Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT: Clin Orthop Rel Res. 2014 Feb, 472:732-9, Epub 2013 Aug 29.
- Minimum Distraction Gap: How Much Ankle Joint Space Is Enough in Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty? Fragomen AT, McCoy TH, Meyers K, Rozbruch SR: HSS J 2014, 10:6-12.
2013
- Circular External Fixator Assisted Ankle Arthrodesis Following Failed Total Ankle Arthroplasty. McCoy TH, Goldman V, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR: Foot Ankle Int. 2012, 33(11):947-955.
- Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society AIM Index Reliably Assesses Lower Limb Deformity McCarthy JJ, Iobst CA, Rozbruch SR, Sabharwal S, Eisman E: Epub ahead of print Oct 2, 2012. Clin Ortho Rel Res. 2013, 471:621-7.
- Growth Arrest of the Tibia after ACL Reconstruction: Lengthening and Deformity Correction with the Taylor Spatial Frame. Rozbruch SR, Schachter L, Bigman D, Marx R: Published online before print April 25, 2013, doi: 10.1177/0363546510369318; Am. J Sports Med, 2013, 41(7):1636-1641.
- Distal Tibial Periarticular Nonunions: Ankle Salvage with Bone Transport. Schottel P, Muthusamy S, Rozbruch SR: J Orthop Trauma. Epub 2013 Sep 26.
- Femoral Deformity Planning: Intentional Placement of the Apex of Deformity, Peter D. Fabricant, MD, MPH; James M. Camara, PhD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Healio.com/orthopedics, Search: 20130426-11, Volume 36, Number 5, May 2013
- Limb Lengthening in children with Russell-Silver syndrome: a comparison to other etiologies; V. Goldman, TH McCoy, MD Harbison, AT Fragomen, SR Rozbruch, Journal of Children's Orthopaedics ISSN 1863-2521, Volume 7, Number 2 (2013)
- Antibiotic-Coated Nail for Fusion of Infected Charcot Ankles, Abhijit Pawar, MD, Goksel Dikmen, MD, Austin Fragomen, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Foot & Ankle International 34(1) 80-84, American Orthopedic Foot & Ankle Society, 2013
2012
- External Fixator Assisted Ankle Arthrodesis Following Failed Total Ankle Arthroplasty, McCoy TH, Goldman V, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR, Foot Ankle Int./ Vol. 33, No. 11, November 2012, 33(11):947-955.
- Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society AIM Index Reliably Assesses Lower Limb Deformity, James McCarthy MD, Christopher A. Iobst MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Sanjeev Sabharwal MD, Emily A. Eismann MS, Clin Orthop Relat Res, DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2609-8, March 2012
- Osteotomy, Arthrodesis and Arthroplasty for Complex Multiapical Deformity of the Leg, Alex C. Lesiak, MD, J. Turner Vosseller, MD, S. Rozbruch, MD, HSS Journal, The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery, ISSN 1556-3316, Volume 8 Number 3 (2012)
- Correction of Proximal Tibia Varus with External Fixation, Kashif Ashfaq, MD, Austin Fragomen, MD, Joseph T. Nguyen, MPH, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, 2012 Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., The Journal of Knee Surgery
- Evidence-Based Indications for Distraction Ankle Arthroplasty, Nichoas C. Smith, MD, BA, Douglas Beaman, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Mark A. Glazebrook, PhD, MD, Foot & Ankle International, 2012, by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society
- Complex Ankle Arthrodesis Using the Ilizarov Method Yields High Rate of Fusion, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, Eugene Borst, BA, Lindsay Schachter, BD, Stephen Lyman, PhD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons 2012
- Bone Tumor Reconstruction with the Ilizarov Method, Thomas H. McCoy Jr., MD, Han Jo Kim, MD, Michael B. Cross, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, John H. Healey, MD, Edward A. Athanasian, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Journal of Surgical Oncology, Wiley Periodicals, Inc, 2012
- Does Humeral Lengthening With a Monolateral Frame Improve Function?, Abhijit Y. Pawar, Thomas H. McCoy, Austin T. Fragomen & S. Robert Rozbruch, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, A Publication of the Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons, (2012) Volume 470. Number 7.
- Does Lengthening and The Plating (LAP) Shorten Duration of External Fixation?, Ryor Harbacheuski MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, A Publication of the Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons, (2012) 470:1771-1781
- Femoral Lengthening with Lengthening of a Nail has Fewer Complications than Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distraction, Shaham Mahboubian, Matthew Seah, Austin T. Fragomen, D. Robert Rozbruch, Clinical Orthopaedic and Related Research, The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons, (2012) 470:1221-1231
2011
- Building for the Future: The transformative leadership of Dean Antonio Gotto, Beth Saulnier, Weill Cornell Medicine Special Issue 2011, The Magazine of Weill Cornell Medical College and Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences, 2011
- What's New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction, Sanjeev Sabharwal, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD in the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, Volume 93-A, Number 24, December 21, 2011
- Lengthening of the Femur Over an Existing Intramedullary Nail, Han Jo Kim, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, Keith Reinhardt, MD, James J. Hutson, Jr, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, Volume 25, Number 11, November 2011
- Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia, Daniel M. Horn, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Food & Ankle International/Vol. 32, No. 10/October 2011
- ORS Virtual Dedicated July issue of the Journal of Orthopaedic Research is focused on The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society
- Femoral Reconstruction Using External Fixation, Yevgeniy Palatnik and S. Robert Rozbruch, Advances in Orthopedics, Volume 2011 (2011).
- Use of Ultrasound in Detection and Treatment of Nerve Compromise in a Case of Humeral Lengthening, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD& Craig Fryman, BS & Daniel Bigman, PA & Ronald Adler, MD, PhD, HSS Journal (2011) 7: 80–84
- Distal Femoral Osteotomy: Is Internal Fixation Better than External? K. T. Matthew Seah BMedSci, MBChB, Raheel Shafi MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2011.
- Comparison of PACS and Hard-copy 51-inch Radiographs for Measuring Leg Length and Deformity, Saurabh Khakharia MD, Daniel Bigman PA-C, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Helene Pavlov MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Clin Orthop Relat Res (2011) 469:244–250.
- Gradual Reduction of Chronic Fracture Dislocation of the Ankle Using Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame, Nazzar Tellisi & Jonathan T. Deland, MD& S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, HSS Journal (2011) 7: 85–88
- Fixator-Assisted Plating of Limb Deformities by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Published by Oper Tech Orhop 21:174-179 (2011)
2010 and earlier
2010
- Lengthening of the Femur over an Existing Intramedullary Nail, Han Jo Kim, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, Keith Reinhardt, MD, James J. Hutson, Jr, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, published by Ortho Trauma (August 25, 2010)
- Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur, Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch, Current Orthopaedic Practice, March/April 2010
- Noninvasive Quantitative Assessment of Bone Healing After Distraction Osteogenesis, Oladapo M. Babatunde, MD & Austin T. Fragomen, MD & S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, HSS Journal, 2010.
- Grand Rounds from HSS: Management of Complex Cases, Winter 2010, Volume 1, Issue 1
- Intraoperative Measurement of Mounting Parameters for the Taylor Spatial Frame, George D. Gantsoudes, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, 2010 Apr;24(4):258-62.
2009
- Does the Taylor Spatial Frame Accurately Correct Tibial Deformities? S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Kira Segal BA, Svetlana Ilizarov MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Gabriel Ilizarov MD, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 2009.
- Limited Quadricepsplasty for Contracture during Femoral Lengthening - Saurabh Khakharia MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD
- Computer Navigation and Fixator-Assisted Femoral Osteotomy for Correction of Malunion After Periprosthetic Femur Fracture - Daniel O. Kendoff, MD, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, Andrew D. Pearle, MD, Mustafa Citak, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- Joint Preservation of the Osteoarthritic Ankle Using Distraction Arthroplasty - Nazzar Tellisi, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Dawn Kleinman, BS; Martin J. O’Malley, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
2008
- Limb Lengthening and Then Insertion of an Intramedullary Nail: A Case-matched Comparison, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Dawn Kleinman BA, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Svetlana Ilizarov MD, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, December 2008.
- Ipsilateral Fibular Transport Using Ilizarov-Taylor Spatial Frame for a Limb Salvage Reconstruction: a Case Report published in HSS Journal: Volume 5, Issue1 (2008)
- Humeral lengthening and deformity correction in Ollier’s disease: distraction osteogenesis with a multiaxial correction frame published by Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics in 2008
- A Biomechanical Comparison of an Intramedullary Nail and Ilizarov External Fixator for Ankle Arthrodesis Foot and Ankle International, March 2008
- Limb Salvage Reconstruction of the Ankle with Fusion and Simultaneous Tibial Lengthening Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame Journal of the Hospital for Special Surgery, March 2008
- Repair of Tibial Nonunions and Bone Defects with the Taylor Spatial Frame, published in Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, February 2008.
2007 and earlier
- Lengthening and Reconstruction of Congenital Leg Deficiencies for Enhanced Prosthetic Wear published by The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons in October, 2007
- Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery: Book Review in Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American, October 2007.
- The Mechanics of External Fixation article in The HSS Journal
- Correction of Tibial Deformity with Use of the Ilizarov-Taylor Spatial Frame article in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (7 mb PDF)
- Drs. Fragomen and Rozbruch publish article on femoral osteotomy in eMedicine from WebMD.
- Dr. Rozbruch publishes Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma (vol. 20, no.6, July 2006)
- Drs. Rozbruch and Ilizarov publish new book on Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction
- Lengthening of a Free Fibular Graft after Sarcoma Resection of a Humerus by Svetlana Ilizarov, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD; and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD from the Institute for Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction (2006)
- Simultaneous Treatment of Tibial Bone and Soft-tissue Defects With the Ilizarov Method, published in Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, March 2006 (pdf)
- Nonunions and Malunions by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD and Kevin Pugh, MD (pdf) published in Orthopaedic Knowledge Update Trauma v.3, 2005.
- Proximal Tibial Osteotomy for Medical Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee Using the Ilizarov-Taylor Spatial Frame (pdf) published in Techniques of Knee Surgery Sept 2005
- Posttraumatic Reconstruction of the Ankle Using the Ilizarov Method published in HSS Journal September 2005 ( Vol 1, number 1, pages 68 - 88)
- IIlizarov Hip Reconstruction for the Late Effects of Infantile Hip Sepsis published in Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (Am), May 2005 (Vol 87-A, number 5, pages 1007-1018)
- Knee Arthrodesis with Simultaneous Lengthening of the Tibia published in Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, March 2005 (Vol 19, number 3, pages 171-179)
- Total Knee Replacement Following Proximal Tibial Osteotomy Dr. Rozbruch's letter to the editor is published in Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Am, November 2004
- Minimal Incision Technique Using a Two-Hole Plate for Fixation of Stable Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures by M. DiPaoli, S. Robert Rozbruch, DL Helfet; published in Orthopedics, Volume 27 Number 23, March 2004
- Ilizarov method for wound closure and bony union of an open grade IIIB tibia fracture John E. Mullen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD; David L. Helfet, MD
- Techniques In Tibial Osteotomy: External Fixation for Proximal Tibial Osteotomy www.hss.edu 2004 March 5.
- Distraction of the Ankle for Arthritis by David John India, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD; Martin J. O'Malley, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD published in Techniques of Foot and Ankle Surgery, December 2003
- Correction of Large Bilateral Tibia Vara Using the Ilizarov Method published by Dr. Rozbruch in Journal of Knee Surgery, January 2003
- Fibula Lengthening Using a modified Ilizarov Method published in Orthopedics, 25:11, November 2002
- Ilizarov Method for Treatment of Extra-Articular Distal Humerus Fractures Article published in Techniques in Shoulder and Elbow Surgery,
3(4)299-305, 2002 - Distraction of Hypertrophic Nonunion of Tibia with Deformity Using Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; David L. Helfet, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD
- Distraction Osteogenesis for Nonunion After High Tibial Osteotomy by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; John E. Herzenberg, MD; Kevin Tetsworth, MD; H. Robert Tuten, MD; Dror Paley, MD
- The Evolution of Femoral Shaft Plating Technique by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Urs Muller, MD; Emanuel Gautier, MD; Reinhold Ganz, MD
- Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher, MD
- Ilizarov Method for Wound Closure and Bony Union of an Open Grade IIIB Tibia Fracture by John E. Mullen, MD S.; Robert Rozbruch, MD; A. A. Blyakher, MD; David L. Helfet, MD
Selected Books/Chapters
Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT: Tibial/Femoral Osteotomy in Andrew Green, MD, and Roman Hayda, MD: Orthopaedic Postoperative Rehabilitation, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2017.
Rozbruch SR, Hamdy R: Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery Case Atlas, Major Reference Work, Springer International Publishing 2015, On line reference and Textbook (3 volumes, 2500 pages)
Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT: Hybrid Lengthening Techniques: Lengthening and then Nailing (LATN), Lengthening and then Plating (LAP) In: Tsuchiya, Kocaoglu, Eralp (Eds.): Advanced Techniques in Limb Reconstruction Surgery, Springer 2015
Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR: Distraction Arthroplasty for Ankle Osteoarthritis. In: Tsuchiya, Kocaoglu, Eralp (Eds.): Advanced Techniques in Limb Reconstruction Surgery, Springer 2015
Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR: Iatrogenic Deformities, In: Sabharwal S: Pediatric Lower Limb Deformities: Principles and Techniques of Management, Springer 2015.
Rozbruch SR: Percutaneous Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using the Ilizarov/ Taylor Spatial Frame. In: Scuderi GR, Tria AJ: Minimally Invasive Surgery in Orthopaedics, (second edition); Springer International Publishing 2015.
Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR: External Fixation. In: edited by Simon Lee and Andrew Hsu: Synopsis of Foot and Ankle Surgery. Thieme Publishers, New York (in progress)
Academic Case Presentations
-S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
-S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
-S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
-S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
-S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
-Austin T. Fragomen, MD
Presentations
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Key Note Speaker at the Peking University 2017 Osteoarthritis International Forum, HangZhou, ZheJiang Province, China, Sept 2017
- Nuvasive Dinner Lecture; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; UVA, New York, NY; May 25, 2017; Femur and Tibia cases using the Precice Internal Lengthening Nail
- Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society Specialty Day; American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; San Diego, CA; March 18, 2017; Best Papers of 2016 Annual Meeting: Oxygen Consumption Testing and Self-reported Outcomes Following Limb salvage with Tibiocalcaneal or Tibio-talo-calcaneal Fusion.
- Hospital for Special Surgery - Hadassah University Medical Center Orthopedic Conference; Hadassah Hospital, Hebrew University; Jerusalem, Israel; January 13, 2017; Lecture: Evolution of Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Visiting Professor, 28th Annual James J. Callahan, MD Lecture on Musculoskeletal Trauma; Stritch School of Medicine, Department of Orthopedic Surgery; Loyola University Medical Center; Chicago, IL; December 1, 2016
- Advances in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction Surgery
- Integrated Fixation for Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction
- Eastern Orthopedic Association Annual Meeting; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Moderator of Symposium: What’s New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction?, New Orleans, LA; October 21, 2016;
- Lengthening and Reconstruction in Kids
- Adult Deformity Correction
- Nuvasive Educational Program at Orthopedic Trauma Association Meeting; Bone Lengthening Using an Internal Motorized Nail; Washington, DC; October 6, 2016; Adult cases using the Precice Internal Lengthening Nail, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- Managing Osteomyelitis in the 21st Century, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; 29th Annual Baltimore Limb Deformity Course; Baltimore, Maryland; August 25, 2016
- Bone Surgery for Soft-tissue Defects
- Femoral Bone Defects
- Ilizarov Reading International Meeting; Invited International Guest Speaker, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Russian Ilizarov Scientific Center for Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics; Kurgan, Russia; June 16-18, 2016
- Enhancements of Bone Healing
- Integrated Fixation for Limb Lengthening
- Japanese Association of External Fixation and Limb Lengthening, 29th Annual Meeting; Invited International Guest Speaker, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Advances in Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery; Kanazawa, Japan; March 19, 2016
- Stryker STAR Ankle Training Course, Tampa, Florida; February 27, 2016, Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Key Note Speaker at the 2016 National Society of Orthopedics and Traumatology of CHILE meeting, invited by the Reconstruction and Bone Lengthening committee (former ASAMI Chile), Vina del Mar, Chile, Nov 2016
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD; "What’s new in Limb Deformity: Foot and Ankle," and "What's new in Limb Deformity: Trauma," presented at the Eastern Orthopaedic Association 47th Annual Meeting, NOLA, October 2016
- Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Session moderator: Foot and Ankle at the Eastern Orthopaedic Association 47th Annual Meeting, NOLA, October 2016
- "Simultaneous acute femoral deformity correction and gradual limb lengthening using the retrograde Precice femoral nail," "Prophylactic pre operative antibiotics have no influence on pin site infection after external fixation," and "Does the surgical outcome of tibial torsion with genu varum produce outcomes similar to those in varus correction alone." Podium presentations presented at the LLRS 25th annual scientific meeting, Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Charleston, SC, July 2016
- International Symposium dedicated to the 95th anniversary of Professor GA Ilizarov, 65th anniversary of the Ilizarov Method, and 45th anniversary of the Russia Scientific Center "Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics." Moderator for Session 11: Foot & ankle deformity correction using the Ilizarov method, Moderators: Austin Fragomen, MD/Andrey Neretin, MD Presenter: "Complex foot and ankle correction with the TSF," and "Ankle distraction arthroplasty for post traumatic osteoarthritis." Kurgan, Russia, Jun 2016
- "Transitioning to the Internal Lengthening Nail," presented at AAOS Specialty Day- LLRS, Orlando, Mar 2016; Austin T. Fragomen, MD
- Post-Traumatic Tibial Defects Treated by the Ilizarov Method; AAOS Annual Meeting, March 24-28, 2015, Mitchell Bernstein, MD, FRCSC; Samir Sabharwal, BA; Jonathan Barclay, BA; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD
- Dealing with Bone Defects of the Foot, Ankle, and Lower Leg; NY Podiatric Clinical Conference, January 23, 2015, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- Distraction Osteogenesis for Brachymetatarsia Clinical Results and Implications on the Metatarsophalangeal Joint, Haleem AM. MD, Balagadde A. BS, Borst E. BS, Fragomen AT. MD and Rozbruch SR. MD, Fellow Research Presentation, June 2014
- Distraction osteogenesis for posttraumatic bone defects of the leg: Comparison of classic versus integrated technique, Bernstein M, Fragomen AT, Sabharwal S, Barclay J, Rozbruch SR, Fellow Research Presentation, June 2014
- Knee Realignment with Osteotomy, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Conservative Management of Knee Arthritis Course, Hospital for Special Surgery, March 28, 2014
- Adult Femur Lengthening Algorithm, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, LLRS Specialty Day, AAOS annual meeting, New Orleans, LA, March 15, 2014
- Congress on Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, LLRS Specialty Day, AAOS annual meeting, New Orleans, LA, March 15, 2014
- Knee Fusion: Indications & Technique, Advanced TSF Course, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Memphis, TN, August 2-3, 2013
- Understanding deformity Correction and TF Principles, Advanced TSF Course, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Memphis, TN, August 2-3, 2013
- Role and Outcome of Gastrocnemius Recession in Tibial Lengthening, Savanaranaraja Muthusamy, MBBS; MS, Samuel Zonshayn, MS II, Eugene W. Borst, BA, Austin T. Fragomen, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, HSS Fellows Research Symposium, June 2013
- Precision of the New Remote Controlled Internal Lengthening Nail, Kirane, Yatin, MBBS, D.Ortho, MS, PhD; Fragomen, Austin, MD; Rozbruch S. Robert, MD, HSS Fellows Research Symposium, June 2013
- Charcot Reconstruction Using External Fixation, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, NY Podiatric Clinical Conference, January 26, 2013
- Limb Lengthening in Children RSS and other etiologies, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Pediatric Endocrine Rounds, Weill Cornell Medical Center, January 22, 2013
- The effect of malalignment on knee joint contact stresses and forces, Reisse, F; Walker, R; Carpanen, D; Imhauser, CW; Koff, MF; Rozbruch, SR; Dowell, JK; Hillstrom, H; Mootanah, R; Anglia Ruskin University
- S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, New York Foot & Ankle Deformity Course, Roosevelt Hotel, October 27, 2012
- Limb Deformity Correction, presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, McGill University Visiting Professor February 29-March 1, 2012
- Hybrid Techniques: The Best of Internal and External Fixation, presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, McGill University Visiting Professor February 29-March 1, 2012
- External Fixators for Complex Cases about the Knee, presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Holiday Total Knee Course; New York City; December 7, 2012
- New York Foot and Ankle Deformity Course, presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, and Austin T. Fragomen, MD, at The Roosevelt Hotel, New York, NY, October 27, 2012
- First Annual Limb Lengthening & Deformity Correction Visiting Professor: S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, McGill University, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery, Shriners Hospital for Children, Canada, March 1, 2012
- The Top 5 Research Questions I Want LLRS to Answer presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting in San Francisco, CA, 2012
- Half Pin Instability in the Modern Circular External Fixator presented by Thomas H. McCoy, Jr. BA; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Kate Meyers, MS; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Biomechanical Comparison of Bone Stability Using Taylor Spatial Frame Struts and Classic Ilizarov Rods presented by Thomas H. McCoy, Jr. BA; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Kate Meyers, MS; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- The LLRS - AIM Limb Deformity Evaluation: A Pilot Study to 10:51 Evaluate Reliability presented by James J. McCarthy, MD; Sanjeev Sabharwal, MD, Christopher Iobst, MD; Viral Jain, MD; Nate Faulkner; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; David Klimaski; Emily Eismann at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Antibiotic Coated Retrograde Intramedullary Nail for Treatment of Infected Ankle Fusion Nonunion and Arthrosis presented by Abhijit Pawar, MD; Goksel Dikmen, MD; Austin Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Complex Ankle Arthrodesis Using the Ilizarov/TSF presented by Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Stephen Lyman, PhD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- External Fixator Assisted Ankle Arthrodesis Following Failed Total Ankle Arthroplasty presented by Thomas McCoy, Jr., BA; Vladimir Goldman, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty: How Much is Enough? presented by Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Kate Meyers, BS; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Humeral Lengthening with Monolateral External Fixation: Functional Outcome presented by Abhijit Pawar, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Hiriklia Bazhani, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Limb Lengthening in Children with Silver - Russell Syndrome: A Comparison to Other Etiologies presented by Vladimir Goldman, MD; Thomas H. McCoy, Jr, BA; Madeleine Harbison, MD; Austin T. Fragomen, MD; Stephen Lyman PhD; S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Femur Deformity CORA Planning: How to Control the CORA Location presented by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD at the annual Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting in Chicago, 2011
- Dr. Rozbruch presents scientific exhibit, poster, and symposium at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual meeting in San Diego, CA, February 14-18, 2007
- Dr. Rozbruch speaks at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Specialty Day, San Diego, CA February 17, 2007
- Dr. Tellisi presents Lengthening and Reconstruction of Congenital Limb Deficiencies for Optimal Prosthetic Wear at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting, San Diego, CA; July 21-23, 2006 (Microsoft Word document)
- Dr. Tellisi presents Limb Salvage Reconstruction of the Ankle with Simultaneous Arthrodesis and Tibial Lengthening at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting, San Diego, CA; July 21-23, 2006 (Microsoft Word document)
- Dr. Fragomen presents A Biomechanical Comparison of Micromotion After Ankle Fusion Using Two Fixation Techniques: IM Nail or Circular Fixation at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting, San Diego, CA; July 21-23, 2006 (Microsoft Word document)
- Dr. Rozbruch presents Lengthening and Then Nailing (LATN) paper at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting, San Diego, CA; July 21-23, 2006 (Microsoft Word document) Dr. Rozbruch presents Femoral Reconstruction using External Fixation paper at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society meeting, San Diego, CA; July 21-23, 2006 (Microsoft Word document)
- Dr. Rozbruch (chairman) and Dr. Fragomen participate in educational conference: Applications of Ilizarov/ Taylor Spatial Frame to Foot and Ankle Reconstruction (pdf)
- Limb Lengthening Specialty Day program chaired by Dr. Rozbruch at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons meeting in Washington DC, Feb. 26, 2005
- Treatment of Tibial Nonunions and Bone Defects with the Ilizarov/ Taylor Spatial Frame podium presentation delivered by Dr. Rozbruch at the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons annual meeting in Washington, DC on Feb. 25, 2005
- Treatment of Tibial Nonunions and Bone Defects with the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame
- Abstract: Lengthening of the Free Fibular Graft after Sarcoma Resection of the Humerus presented to The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society: ASAMI–North America Fourteenth Annual Scientific Meeting
- Abstract: Pain Control for Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery presented to The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society: ASAMI–North America Fourteenth Annual Scientific Meeting
- Abstract: Correction of Tibial Deformity using the Ilizarov/ Taylor Spatial Frame presented to The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society: ASAMI–North America Fourteenth Annual Scientific Meeting
- Abstract: Treatment of Nonunions and Bone Defects of the Tibia with the Ilizarov/ Taylor Spatial Frame presented to The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society: ASAMI–North America Fourteenth Annual Scientific Meeting
- Abstract: Use of an Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame in Patients with Total Joint Replacement presented to The Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society: ASAMI–North America Fourteenth Annual Scientific Meeting
- "The ISKD Nail" Lecture given by Dr. Rozbruch at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons meeting, March 2004
- "Post-Traumatic Reconstruction of the Foot and Ankle" Lecture given by Dr. Rozbruch at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons meeting, March 2004
- "Bone Transport with TSF" by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
- Dr. Rozbruch trains other surgeons in ISKD course
- Simultaneous Treatment of Bone and Soft-tissue Defects with the Ilizarov Method presented at Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society annual meeting July 2003 and Orthopaedic Trauma Association annual meeting October 2003
- The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Bone Lengthening presented at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society annual meeting July 2003
- Technical Tips to help Optimize the use of the Taylor Spatial Frame presented at the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society annual meeting July 2003
- Ankle Fusion with Simultaneous Lengthening using the Ilizarov Method abstract presented at Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society annual meeting July 2003 and Orthopaedic Trauma Association annual meeting October 2003
- Dr. Rozbruch was a member of the faculty of the Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction Society Specialty Day at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting, February 8, 2003 in New Orleans.
- Abstract: Knee Arthrodesis and Simultaneous Leg Lengthening Using the Ilizarov Method by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD; David L. Helfet, MD; Russell F. Warren, MD
- Abstract: Lengthening and Then Nailing (LATN) of the Tibia by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD
- Abstract: Limited Quadricepsplasty During Femoral Lengthening by S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Arkady Blyakher, MD
- Dr. Rozbruch's participation in the Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction Society Annual Meeting and the Essentials Course in Dallas, Texas- June 7 - 11, 2002
- Dr. Rozbruch was on the faculty of two national Ilizarov courses in Atlanta, Georgia during April 2002. His lectures included:
1. Postoperative Management of Distal Tibia Periarticular Fractures
2. Surgical Techniques of Osteotomy and Corticotomy
3. Postoperative Management of Deformity Corrections
Quality Metrics
Quality Metrics are standards of measurement by which efficiency, performance, progress, or quality of a plan, process, or product can be assessed. We have measured our clinical outcomes for the conditions that we treat. Some of these outcomes have been published in the following peer-review journals.
2019
Sculco PK, Kahlenberg CA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Management of Extra-articular Deformity in the Setting of Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019 Jan 7. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-18-00361. [Epub ahead of print], PMID: 30624304
Extra-articular deformities of the femur and tibia in conjunction with advanced knee osteoarthritis pose unique challenges for the arthroplasty surgeon. Careful preoperative planning is needed to evaluate both the intra- and extra-articular deformities and to determine the best route to total knee arthroplasty.
Steinhaus ME, Buksbaum J, Eisenman A1, Kohli M, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Postoperative Blood Loss in Distal Femoral Osteotomy. J Knee Surg. 2019 Feb 12. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1678540. [Epub ahead of print]
Blood loss remains a significant source of morbidity and mortality in orthopaedic surgery. Administration of tranexamic acid (TXA) resulted in less postoperative blood loss during distal femoral osteotomy (DFO), with the most pronounced effect in those who receive two doses.
Da Cunha RJ, Kraszewski AP, Hillstrom HJ, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain. HSS J, Open AccessOriginal Article, First Online: 19 March 2019
Bilateral proximal tibial osteotomy (PTO) may be effective in improving knee biomechanics during gait and correcting mechanical alignment in patients with bilateral genu varum. Patients also demonstrated improvement in functional outcome scores. Bilateral PTO should be considered in patients with varus knee osteoarthritis in the setting of genu varum to alleviate symptoms and potentially decrease further clinical deterioration.
Gruskay JA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Idiopathic Rotational Abnormalities of the Lower Extremities in Children and Adults. JBJS Rev. 2019 Jan;7(1):e3. doi:10.2106/JBJS.RVW.18.00016. PMID: 30624306
Full text Rotational malalignment of the lower extremity is a potential cause of hip, knee, and ankle pain. Surgical correction of rotational malalignment of the femur and tibia is reserved for severe, symptomatic deformity.
Makhdom AM, Fragomen A, Rozbruch SR. Knee Arthrodesis After Failed Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 Apr 3;101(7):650-660. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.18.00191
Full text Knee arthrodesis after failure of a total knee arthroplasty (TKA) because of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) may provide superior functional outcome and ambulatory status compared with above-the-knee amputation.The use of an intramedullary nail (IMN) for knee arthrodesis following removal of TKA components because of a PJI may result in higher fusion rates compared with external fixation devices.
Morgan OJ, Hillstrom HJ, Ranawat A, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR, Hillstrom R. Effects of a medial knee unloading implant on tibiofemoral joint mechanics during walking. J Orthop Res. 2019 May 23. doi: 10.1002/jor.24379. [Epub ahead of print]
The Atlas™ unicompartmental knee system is a second-generation extra-articular unloading implant for patients with mild to moderate medial knee osteoarthritis. From a biomechanical perspective, extra-articular joint unloading may serve as a treatment option for patients recalcitrant to conservative care. Evaluation of mechanical changes in the tibiofemoral joint demonstrate the potential treatment mechanism of the Atlas™, in accordance with the available clinical data.
Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. The PRECICE magnetic intramedullary compression nail for long bone nonunions; a preliminary report. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, accepted
2018
Iobst CA, Rozbruch SR, Nelson S, Fragomen AT. Simultaneous Acute Femoral Deformity Correction and Gradual Limb Lengthening Using the Retrograde Precice Femoral Nail: Technique and Clinical Results. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018 Apr 1;26(7):241-250. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00573.
The Precice nail was effectively used to correct both limb-length discrepancy and deformity, with excellent overall outcomes. This surgical technique may help avoid the complications that can occur with prolonged postoperative use of an external fixator.
Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Does the surgical correction of tibial torsion with genu varum produce outcomes similar to those in varus correction alone? J Knee Surg. 2018 Apr;31(4):359-369. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1603797. Epub 2017 Jun 24.
The aim of this article is to study the relationship between tibia vara and external tibial torsion in adults. Based on the finding of this analysis, the incidence of rotational malalignment with genu varum is close to 50%. The recognition of this close association between external tibial torsion and tibia vara may allow for further insight into the role of rotation in varus deformity-related knee pathology and treatment. Patients can expect nearly identical outcomes.
James E, Corpus K, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy, Microfracture, and Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate for Treatment of Varus Deformity and Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Ann Sports Med Res 2017, 4(2):110.
This report presents two patients with varus deformity and extensive grade IV medial compartment osteoarthritis treated with medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy (HTO) and microfracture augmented with bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC). Results demonstrate restoration of a neutral mechanical axis, filling of the osteochondral defect, and improvement in subjective outcome scores.
Rozbruch SR. Adult Post-traumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2017 Jun; 31 Suppl 2:S14-S19. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000843.
A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has reliable remote-controlled mechanisms. This allows accurate and well-controlled distraction rate and rhythm, and early clinical results have been very positive.
Kleeblad LJ, van der List JP, Pearle AD, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Feasibility of correcting the mechanical axis in large varus deformities with medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018 Feb;33(2):372-378. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.09.052. Epub 2017 Oct 5.
Patients with large preoperative varus deformities (7°-18°) could be considered candidates for medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA), as 98% were corrected to optimal or acceptable alignment, although cautious approach is needed in deformities >15°. Furthermore, it was noted that the feasibility of achieving optimal alignment could be predicted using the preoperative mechanical axis angle (MAA), joint line congruency angle (JLCA), and age
Hammouda AI, Standard S, Herzenberg JE, Rozbruch SR. Humeral Lengthening with the PRECICE magnetic lengthening nail. HSS J. Accepted Sept 2017.
Intramedullary lengthening nails can provide successful and safe humeral lengthening. Specifically, the PRECICE nail has accurate control over the lengthening process.
Fragomen AT, Kurtz A, Barclay JR, Nguyen J, Rozbruch SR. A comparison of femoral lengthening methods favors the magnetic internal lengthening nail when compared with lengthening over a nail. HSS J. 2018 Jul;14(2):166-176. doi: 10.1007/s11420-017-9596-y. Epub 2018 Jan 5.
Femoral lengthening with magnetic internal lengthening nail (ILN) was more accurate than with lengthening over nail (LON). The magnetic ILN comports the additional advantage of greater precision with distraction rate control and fewer complications. Both techniques afford reliable healing and do not significantly affect knee motion at the final follow-up. The magnetic ILN method showed no superiority in regenerate quality and healing rate.
Harkin E, Rozbruch SR, Liskutin T, Hopkinson W, Bernstein M. Total Hip Arthroplasty And Femoral Nail Lengthening For Hip Dysplasia And Limb Length Discrepancy. Arthroplast Today. 2018 May 3;4(3):279-286. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2018.03.001. eCollection 2018 Sep.
Staged ipsilateral total hip arthroplasty and retrograde intramedullary femoral nail lengthening allows for the correction of both deformity and limb-length discrepancy. Our results report leg-length equalization, independent ambulation without assistive devices, and excellent bone and functional outcomes without complications, demonstrating that this combined technique can be used to achieve targeted lengthening and deformity correction.
Buly RL, Sosa B, Poultsides L, Caldwell E, Rozbruch SR. Femoral Derotation Osteotomy in Adults with Version Abnormalities. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018 Oct 1;26(19):e416-e425. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00623.
A closed, subtrochanteric derotation osteotomy of the femur is a safe and effective procedure to treat either femoral retroversion or excessive anteversion. Excellent or good results were obtained in 93%, despite the need for subsequent implant removal in more than two-thirds of the patients.
Fragomen AT, Kurtz AM, Wagner PJ, Nguyen J, Liu SS, Rozbruch SR. Anesthesia for removal of external fixation with hydroxyapatite-coated half pins. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr 2018;4:90-6.
IV sedation administered in the operating room provided adequate pain control to perform fixator removal and pin site debridement in most cases. Removal of external fixation used for foot and ankle reconstruction may be more painful.
Sheeha ED, Steinhaus ME, Kim HJ, Cunningham ME, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Leg-Length Discrepancy, Functional Scoliosis, and Low Back Pain. JBJS Rev. 2018 Aug;6(8):e6. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00148
Patients with a limb length discrepancy (LLD), low back pain, and functional scoliosis should undergo radiographic evaluation with the pelvis leveled using blocks placed under the shorter limb. When the LLD or symptoms are minimal, patients may benefit from a shoe lift. Patients with an LLD of 20 mm may be considered for operative intervention.
Hamdy RC, Bernstein MA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. What's New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017 Aug 16;99(16):1408-1414. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.17.00464.
This specialty update provides a summary of the most impactful articles related to limb alignment, limb lengthening, and joint preservation that were published in 2017.
Lam A, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia. Hand (N Y). 2017 Oct 1:1558944717736859. doi: 10.1177/1558944717736859. Epub ahead of print.
Progressive distraction osteogenesis can obtain functionally successful results and improvement in aesthetics and body image without severe complications in skeletally mature adults with brachymetacarpia.
Vulcano E, Markowitz JM, Ali S, Nguyen J, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density. JAAOS - Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. September 15, 2018 - Volume 26 - Issue 18 - p e388–e394 doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00949.
This study suggests that there may be a correlation between pixel density ratio (PDR) and clinical bone healing, and should be followed by additional studies to understand the relationship between PDR and bony union.
Richardson SS, Schairer WW, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Cost Comparison of Femoral Distraction Osteogenesis With External Lengthening Over a Nail Versus Internal Magnetic Lengthening Nail. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00741. [Epub ahead of print]
Although implants are more expensive for magnetic lengthening nails (MLN) than lengthening over nail (LON), this appears to be offset by fewer procedures. Overall, the two procedures had similar total costs, but MLN was associated with a decreased number of procedures and shorter time to union.
Bernstein M, Fragomen A, Rozbruch SR. Tibial Bone Transport Over an Intramedullary Nail Using Cable and Pulleys. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2018 Mar 28;8(1):e9. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.17.00035. eCollection 2018 Mar 28
Massive bone defects (>8 cm) will not unite without an additional intervention., and require a predictable, durable, and efficient method to regrow bone. Our technique of tibial bone transport over an intramedullary nail using cable and pulleys combines internal and external fixation, allowing the external fixator to be removed at the end of the distraction phase. This increases the efficiency of limb reconstruction and decreases complications associated with external-fixators.
Green SA, Fragomen AT, Herzenberg JE, Iobst C, McCarthy JJ, Nelson SC, Rozbruch SR, Standard S. A magnetically controlled lengthening nail: A prospective study of 31 individuals (The PRECICE™ intramedullary nail study). J Limb Lengthen Reconstr 2018;4:67-75.
The PRECICE™ IM nail is a well-tolerated, reliable, fully implantable limb lengthening device that accurately elongates the femur or tibia in a variety of causes of limb length inequality, with a low implant failure rate, and few complications.
2017
Fragomen AT. Transitioning to an Intramedullary Lengthening and Compression Nail. J Orthop Trauma Vol 31, Number 6 Supplement, June 2017.
The Intramedullary lengthening nail has allowed for treatment of tibia and femur problems without the use of an external device.
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail. S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. J Orthop Trauma Vol 31, Number 6 Supplement, June 2017. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000843.
Intramedullary lengthening is effective in treating deformity and shortening of tibial malunion and posttraumatic growth arrest of the femur.
Humerus Lengthening With the PRECICE Internal Lengthening Nail. Anton M. Kurtz, MD and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. J Pediatr Orthop Vol 37, Number 4, June 2017. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000941.
Intramedullary lengthening works well in the humerus.
Rozbruch SR. Why are we special? Limb deformity is more than an overlapping subspecialty. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr 2017;3:1-3.
Limb lengthening reconstruction is a specialization that is unique from the classical orthopedic specialties and is a practice that is proving to be more and more necessary.
Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. Tibial/Femoral Osteotomy. In Green A, and Hayda R: Orthopaedic Postoperative Rehabilitation. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 2017
Prescribed exercises after surgery are effective in preventing joint stiffness.
2016 and earlier
2106
Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty: Indications, Technique, and Outcomes. Mitchell Bernstein, Jay Reidler, Austin Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2016;0:1-11. DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00077
Ankle distraction is a reliable alternative to ankle arthrodesis or total ankle arthroplasty in young patients with arthritis. Although the initial goal of ankle distraction is to ankle arthrodesis many patients achieve the lasting benefit of the eliminating the need for ankle arthroplasty or fusion completely.
Prophylactic Postoperative Antibiotics May Not Reduce Pin Site Infections After External Fixation. Austin T. Fragomen, Andy O. Miller, Barry D. Brause, Vladimir Goldman, and S. Robert Rozbruch. The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. Vol. 12 No. 3; October 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11420-016-9539-z
Pin infection is a common problem at pin sites. Prophylactic antibiotics do not aid in the prevention of pin site infections in any way and should not be used on healthy patients.
Neglected Patellar Tendon Rupture with Massive Proximal Patellar Migration Treated with Patellar Transport and Staged Allograft Reconstruction. Osama Elattar, MD, Struan H. Coleman, MD, Russell F. Warren, MD,and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. The Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 4(11), 2325967116672175. DOI: 10.1177/2325967116672175
For patients with soft tissue contractures, adhesions, and fixed proximal patellar migration the use of pins and wires for external fixation is an effective way to treat and salvage neglected patellar tendon rupture.
Validation of a modified Scoliosis Research Society instrument for patients with limb deformity: The limb deformity—Scoliosis Research Society (LD-SRS) score. Peter D. Fabricant, Eugene W. Borst, Stuart A. Green, Robert G. Marx, Austin T. Fragomen, and S. Robert Rozbruch. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2.
The new scale LD-SRS was shown to give a more accurate description of the quality of life in regards to people with nonarthritic lower extremity deformity than the global quality of life measurements.
Gradual correction of knee flexion contracture using external fixation. Ettore Vulcano, Jonathan S. Markowitz, Austin T. Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2.
Circular external fixation was found to be a reliable way of treating knee flexion contractures and concurrent ankle equinus as long as the correction with a brace continued on for 1-3 months following surgery.
Oxygen consumption testing and self-reported outcomes following limb salvage with tibiocalcaneal or tibio-talo-calcaneal fusion. S. Robert Rozbruch, Joshua R. Buksbaum, Austin T. Fragomen, Eugene W. Borst, Polly DeMille. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Jul‑Dec 2016, Vol 2, Issue 2
Although our complex ankle fusion patients have elevated oxygen consumption levels compared to normal subjects, they have lower oxygen consumption levels than amputees, and thus are able to walk while consuming less energy.
Open Wedge Distal Femoral Osteotomy: Accuracy of Correction and Patient Outcomes. Osama Elattar, Ishaan Swarup, Aaron Lam, Joseph Nguyen, Austin Fragomen and S. Robert Rozbruch. The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. 5 July 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11420-016-9516-6
Distal femoral osteotomy was found to be a reliable procedure to treat valgus knee malalignment with accurate deformity correction and clinical improvement post surgery.
The use of blocking screws with internal lengthening nail and reverse rule of thumb for blocking screws in limb lengthening and deformity correction surgery. Muthusamy S, Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. Strat Traum Limb Recon. 11 September 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0265-3
Common deformities that occur in femur and tibia osteotomies during the use of internal lengthening can be prevented with the use of blocking screws. The reverse rule of thumbs is useful for placing blocking screws.
What's New in Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction. Hamdy RC, Bernstein MA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 17 August 2016. DOI 10.2106/JBJS.16.00460
Limb reconstruction is a fast growing practice with many new techniques appearing, this paper summarizes our most recent techniques.
Lengthening of the Femur with a Remote-Controlled Magnetic Intramedullary Nail: Retrograde Technique. Austin T. Fragomen, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, JB&JS Essential Surgical Techniques, Volume 6, Issue 2, May 11, 2016
When fixing a distal femoral deformity the retrograde technique is more effective than the antegrade technique and allows for corrections of distal deformities when the osteotomy is done at the time of the nail.
Prevention of pin site infection in external fixation: A review of the literature. Kazmers NH, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction. 3 May 2016. DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0256-4.
There is no clear way to avoid infection in the pin sites of external fixators; however, many techniques are commonly used by surgeons to minimize the risk.
External fixation reconstruction of the residual problems of benign bone tumours. Levent Eralp, F. Erkal Bilen, S. Robert Rozbruch, Mehmet Kocaoglu, Ahmed I. Hammoudi. Strategies in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction, 26 January 2016.
The use of external fixators and distraction osteogenesis are effective in treating benign bone tumors and at minimizing the risk of recurrence of deformity.
Lengthening of the Femur with a Remote-Controlled Magnetic Intramedullary Nail: Antegrade Technique. S. Robert Rozbruch, Austin T. Fragomen. JB&JS Essential Surgical Techniques, Volume 6, Issue 1, January 13, 2016.
The intramedullary nail is good for lengthening of the femur as well as angular and deformity correction.
2015
Talar body fracture nonunion and osteonecrosis with adjacent arthritis can be successfully treated with tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis using circular external fixation. Eugene Wilson Borst, Scott J. Ellis, Austin Thomas Fragomen. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Oct-Dec 2015, Vol 1, Issue 1.
Circular external fixation was used for the first time to simultaneously treat a complex talus nonunion as well as ankle and subtalar arthritis. Our patient has been pain free, in neutral alignment, and back to normal activity after this complex TTC fusion.
Distraction osteogenesis for brachymetatarsia: Clinical results and implications on the metatarsophalangeal joint, Amgad M. Haleem, Angela Balagadde, Eugene Wilson Borst, Huong T. Do, Austin Thomas Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. Journal of Limb Lengthening & Reconstruction. Oct-Dec 2015, Vol 1, Issue 1.
DO is an effective method to treat brachymetatarsia, with high patient satisfaction. Larger studies are required to further investigate MTP joint complications and the optimal method of stabilization of the distraction.
Complex Ankle Arthrodesis: Review of the literature, Remy V Rabinovich, Amgad M Haleem, S Robert Rozbr. World Journal of Orthopedics, 2015 September 18; 6(8): 602-613 ISSN 2218-5836.
This article discusses the literature surrounding complex ankle arthrodesis, namely the risk factors, surgical techniques (internal vs. external fixation), and various methods to accelerate healing at the fusion site.
Skeletal Repair in Distraction Osteogenesis: Mechanisms and Enhancements, Jocelyn Compton, Austin Fragomen, S. Robert Rozbruch. JBJS Reviews, Volume 3, Issue 8, August 2015, DOI 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.N.00107.
This article explores what distinguishes Distraction osteogenesis bone healing from typical fracture healing, and explains the numerous adjuncts to accelerate osteogenesis and risk factors associated with the procedure.
Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery Case Atlas, Springer International Publishing, Editors: Rozbruch, S. Robert, Hamdy, Reggie (Eds.) Copyright: 2015.
3 book set, 2500 pages. The atlas features six sections all pertaining to limb deformity correction: Pediatric Deformity, Trauma, Foot & Ankle (edited by Dr. Fragomen), Adult Deformity (edited by Dr. Rozbruch), Tumor, and Upper Extremity.
What is the Utility of a Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Service in an Academic Department of Orthopaedic Surgery?; S. Robert Rozbruch, Elizabeth S. Rozbruch, Samuel Zonshayn, Eugene W. Borst & Austin T. Fragomen. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. Volume 473, Number 4; DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4267-0.
Based on referral data, surgical diversity, and academic productivity, our practice highlights the utility of a Limb Deformity Service to an academic hospital.
2014
Does Integrated Fixation Provide Benefit in the Reconstruction of Post-Traumatic Tibial Bone Defects?; Symposium: 2014 Annual Meeting of the Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society; Mitchell Bernstein MD, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Samir Sabharwal BA, Jonathan Barclay BA, S. Robert Rozbruch MD. Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4326-6.
Integrated fixation reduces time in external fixation while increasing surgical efficiency of tibial reconstruction as compared to exclusive use of external fixation.
Metatarsophalangeal Arthritis Following Fourth Metatarsal Lengthening Treated With Distraction Arthroplasty: Case Report, Amgad M. Haleem, Douglas N. Mintz and S. Robert Rozbruch. Foot Ankle Int 2014 35: 1075 originally published online 18 July 2014 DOI: 10.1177/1071100714543648.
Iliac Crest Bone Marrow Aspirate injections and distraction arthroplasty of the Metatarsophalangeal joint can effectively combat arthritis and stiffness in the joint after distraction osteogenesis of the metatarsal due to brachymetatarsia.
Knee Arthrodesis as Limb Salvage for Complex Failures of Total Knee Arthroplasty, Raul Kuchinad, MD, FRCSC, Mitchell S. Fourman, MD M.Phil, Raul Kuchinad, MD, FRCSC, Mitchell S. Fourman, MD M.Phil. The Journal of Arthroplasty 29 (2014) 2150–2155.
Bone loss, soft tissue envelope, and overall bone health determine the best method of knee arthrodesis for limb salvage after a complex failed Total Knee Replacement. Knee arthrodesis is an effective technique for limb salvage after complex failure and infection following knee replacement.
Neglected rotatory knee dislocation: A case report, Saker Khamaisy, Amgad M. Haleem, Riley J. Williams, S. Robert Rozbruch, S. Khamaisy et al. / The Knee 21 (2014) 975–978.
A unique rotary knee dislocation, in addition to a lateral patellofemoral dislocation was effectively treated after 3 years of neglect with a Taylor Spatial frame and multiple surgeries.
What Risk Factors Predict Usage of Gastrocsoleus Recession During Tibial Lengthening? S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Samuel Zonshayn BA, Saravanaraja Muthusamy MBBS, MS, Ortho, Eugene W. Borst BA, Austin T. Fragomen MD, Joseph T. Nguyen MPH. Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3526-9.
Patients with tibial lengthening greater than 42 mm or 13% of the overall segment lengths, as well as those with a congenital LLD are more likely to undergo a gastroc-soleus Recession during Tibia lengthening.
Motorized Intramedullary Nail for Management of Limb-length Discrepancy and Deformity. S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; John G. Birch, MD; Mark T. Dahl, MD; John E. Herzenberg, MD. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2014;22:403-409, July 2014, Vol 22, No 7.
Motorized Intramedullary Nails can lengthen both Femurs and Tibias internally, obviating the need for external fixation while providing stable fixation and lengthening.
Development and validation of a computational model of the knee joint for the evaluation of surgical treatments for osteoarthritis. R. Mootanah, C.W. Imhauser, F. Reisse, D. Carpanen, R.W. Walker, M.F. Koff, M.W. Lenhoff, S.R. Rozbruch, A.T. Fragomen, Z. Dewan, Y.M. Kirane, K. Cheah, J.K. Dowella and H.J. Hillstrom. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 2014 Vol. 17, No. 13, 1502–1517.
The computational knee model can accurately predict normalized intra-articular pressures and forces for different loading conditions, and could be further tuned to account for different surgical procedures.
Precision of the PRECISE® Internal Bone Lengthening Nail, Yatin M. Kirane, Austin T. Fragomen, and S. Robert Rozbruch. Clin Orthop Relat Res. ISSN 0009-921X, DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-3575-0, 2014.
The PRECICE Internal Lengthening nail accurately and precisely lengthens bone, with minimal impact on knee and ankle range of motion and complications.
Recombinant Human BMP-2 Increases the Incidence and Rate of Healing in Complex Ankle Arthrodesis, Fourman MS, Borst EW, Bogner E, Rozbruch SR, Fragomen AT. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 2014 Feb, 472:732-9, Epub 2013 Aug 29.
Recombinant Human BMP-2 were significantly more likely to obtain fusion after initial surgery and spend less time in external fixation, while showing significantly more bone bridging on radiographic analysis.
Minimum Distraction Gap: How Much Ankle Joint Space Is Enough in Ankle Distraction Arthroplasty? Fragomen AT, McCoy TH, Meyers K, Rozbruch SR. HSS J 2014, 10:6-12.
Six mm of minimum tibiotalar joint distraction is sufficient to prevent contact between the tibia and talus during ankle distraction arthroplasty.
2013
Circular External Fixator Assisted Ankle Arthrodesis Following Failed Total Ankle Arthroplasty. McCoy TH, Goldman V, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR: Foot Ankle Int. 2012, 33(11):947-955.
External Fixation and possible tibia lengthening, provides an excellent method with a high fusion rate to combat bone loss and possible infection after failed total ankle arthroplasty.
Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society AIM Index Reliably Assesses Lower Limb Deformity. McCarthy JJ, Iobst CA, Rozbruch SR, Sabharwal S, Eisman E: Epub ahead of print Oct 2, 2012. Clin Ortho Rel Res. 2013, 471:621-7.
Growth Arrest of the Tibia after ACL Reconstruction: Lengthening and Deformity Correction with the Taylor Spatial Frame. Rozbruch SR, Schachter L, Bigman D, Marx R: Published online before print April 25, 2013, doi: 10.1177/0363546510369318; Am. J Sports Med, 2013, 41(7):1636-1641.
Tibia lengthening using TSF can counter acute deformity in the tibia stemming from a growth arrest after ACL reconstruction in skeletally immature patients.
Distal Tibial Periarticular Nonunions: Ankle Salvage with Bone Transport. Schottel P, Muthusamy S, Rozbruch SR. J Orthop Trauma. Epub 2013 Sep 26.
Nonunions in the distal tibia can be challenging due to the lack of bone stock in the area. However, a three ring, double osteotomy frame can be used to excise the infected bone and transporte proximal tibial bone to overcome the nonunion.
Femoral Deformity Planning: Intentional Placement of the Apex of Deformity, Peter D. Fabricant, MD, MPH, James M. Camara, PhD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Healio.com/orthopedics, Search: 20130426-11, Volume 36, Number 5, May 2013.
Intentional placement of a single osteotomy can be used to correct a multiapical deformity in the distal femur to minimize translation.
Limb Lengthening in children with Russell-Silver syndrome: a comparison to other etiologies; V. Goldman, TH McCoy, MD Harbison, AT Fragomen, SR Rozbruch. Journal of Children's Orthopaedics ISSN 1863-2521, Volume 7, Number 2 (2013).
Patients with Russell-Silver syndrome treated for Limb Length discrepancies healed faster than other patients treated for LLDs.
Antibiotic-Coated Nail for Fusion of Infected Charcot Ankles, Abhijit Pawar, MD, Goksel Dikmen, MD, Austin Fragomen, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Foot & Ankle International 34(1) 80-84, American Orthopedic Foot & Ankle Society, 2013.
Antibiotic-coated retrograde nails were successfully used to achieve bony union, fusion of the ankle joint, and elimination of infection in our patients with infected Charcot ankles.
2012
Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society AIM Index Reliably Assesses Lower Limb Deformity, James McCarthy MD, Christopher A. Iobst MD, S. Robert Rozbruch MD, Sanjeev Sabharwal MD, Emily A. Eismann MS, Clin Orthop Relat Res, DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2609-8, March 2012.
The LLRS’s AIM rating reliably classifies the complexity of a lower limb deformity.
Osteotomy, Arthrodesis and Arthroplasty for Complex Multiapical Deformity of the Leg, Alex C. Lesiak, MD, J. Turner Vosseller, MD, S. Rozbruch, MD, HSS Journal, The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery, ISSN 1556-3316, Volume 8 Number 3 (2012).
Post-traumatic multiapical tibia deformities can be effectively treated with ankle fusion, tibial osteotomy, and total knee replacement. Techniques from less complex deformities are used in conjunction to attain pain relief and deformity correction in more complex cases.
Evidence-Based Indications for Distraction Ankle Arthroplasty, Nichoas C. Smith, MD, BA, Douglas Beaman, MD, S. Robert Rozbruch, MD, Mark A. Glazebrook, PhD, MD, Foot & Ankle International, 2012, by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society.
There is inadequate evidence in the literature to refute or support the currently accepted indications for Ankle distraction-osteogenesis.
For general questions, please contact a staff member of Dr. Rozbruch's or Dr. Fragomen's office.